Mader - Biology - 11e, solutions manual and test bank 0073525502
Biology by Sylvia Mader and Michael Windelspecht- 11e, solutions manual and test bank 0073525502
Mader - Biology - 11e, TEST BANK 0073525502
ch2 Key
| 1. | Which of the following elements would be more reactive with other elements? |
| Blooms Level: 3. Apply
Chapter - Chapter 02 #1
Learning Outcome: 02.01.04 Determine how electrons are configured around a nucleus.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 2. | Which of the following would be a proposed mechanism by which stomach antacids work? | A. | Antacids dilute the solution, therefore lowering the pH. | | B. | Antacids are bases and by definition can absorb H+ out of a solution. | | C. | Antacids are bases and by definition can absorb OH- out of a solution. | | D. | Antacids contain mostly water and so they neutralize the solution. | |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #2
Learning Outcome: 02.04.03 Analyze how buffers prevent large pH changes in solutions.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 3. | If you place the corner of a paper towel into a droplet of water the water moves across the paper towel. Which of the following would explain the movement of the water? | D. | both cohesion and adhesion | |
| Blooms Level: 3. Apply
Chapter - Chapter 02 #3
Learning Outcome: 02.03.01 Describe how water associates with other molecules in solution.
Section: 02.03
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 4. | Which of the following elements is NOT one of the six most common elements in living organisms? Incorrect Answers: A. Carbon is one of the six most common elements in living organisms. |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #4
Learning Outcome: 02.02.01 Describe how elements are combined into compounds and molecules.
Section: 02.02
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 5. | If the atomic number of an element is 6 and the atomic mass is 12.01, how many protons are there in the nucleus? |
| Blooms Level: 3. Apply
Chapter - Chapter 02 #5
Learning Outcome: 02.01.02 Use the periodic table to evaluate relationships between atomic number and mass number.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 6. | Which of the following is/are an atom, an isotope and an ion? | E. | All of the choices are atoms, isotopes and ions. | |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #6
Learning Outcome: 02.01.03 Describe how variations in an atomic nucleus account for its physical properties.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
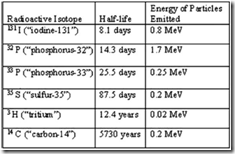
| 7. | From the above table of radioisotopes and their properties, it is obvious that | A. | the longer the half-life, the more energy emitted by the particles. | | B. | the longer the half-life, the less energy emitted by the particles. | | C. | radioisotopes of the same element must emit the same amount of energy in their emissions and decay at the same rate. | | D. | adjusted for time, radioisotopes emit the same amount of energy in their emissions. | | E. | energy and half-life are not directly related. | |
| Blooms Level: 3. Apply
Chapter - Chapter 02 #7
Learning Outcome: 02.01.03 Describe how variations in an atomic nucleus account for its physical properties.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 8. | Which statement is NOT true about subatomic particles? | A. | Protons are found in the nucleus. | | B. | Neutrons have no electrical charge. | | C. | Electrons contain much less mass than neutrons. | | D. | Electrons are found in orbitals around the nucleus. | | E. | All electrons in an atom contain the same amount of energy. | Incorrect Answers: A. It is true that protons are found in the nucleus. |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #8
Learning Outcome: 02.01.01 Describe how protons, neutrons, and electrons relate to atomic structure.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 9. | Which is NOT true about the electrical charges in chemistry? | A. | Protons carry a positive charge. | | B. | In an atom, the number of protons and neutrons must be equal. | | C. | An atom is neutral when the positive and negative charges balance. | | D. | An ion contains one or more positive or negative charges. | Incorrect Answers: A. It is true that protons carry a positive charge. |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #9
Learning Outcome: 02.01.01 Describe how protons, neutrons, and electrons relate to atomic structure.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 10. | In a water molecule, | A. | the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms. | | B. | the oxygen atom has an overall negative charge with the hydrogen atoms having an overall positive charge. | | C. | unequal sharing of electrons results in a polar molecule. | | D. | All of the choices are correct. | |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #10
Learning Outcome: 02.02.03 Compare the relative strengths of ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds.
Section: 02.02
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 11. | An atom's atomic mass is best described as the mass of | A. | the protons it contains. | | B. | the neutrons it contains. | | C. | electrons in the outermost shell. | | D. | protons and neutrons it contains. | | E. | protons and electrons it contains. | |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #11
Learning Outcome: 02.01.02 Use the periodic table to evaluate relationships between atomic number and mass number.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 12. | A research article indicates that researchers have used an isotope 3H to trace a certain metabolic process. From the symbol that is given, we know this is a hydrogen isotope with | D. | one proton and two neutrons. | | E. | two protons and one neutron. | |
| Blooms Level: 3. Apply
Chapter - Chapter 02 #12
Learning Outcome: 02.01.03 Describe how variations in an atomic nucleus account for its physical properties.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 13. | Both 18O and 16O are found in nature. However, 16O is the most common. Therefore, | A. | these are different elements. | | B. | oxygen atoms can have eight or 10 neutrons. | | C. | 18O has two additional electrons in its outer shell. | | D. | 18O is the form of oxygen that provides living cells with life. | | E. | only the common form of 16O can bond with hydrogen atoms to form H2O. | |
| Blooms Level: 3. Apply
Chapter - Chapter 02 #13
Learning Outcome: 02.01.01 Describe how protons, neutrons, and electrons relate to atomic structure.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 14. | To determine the age of fairly recent fossils and organic artifacts, it is possible to analyze the amounts of the isotopes 14C and 14N, because over time the 14C-which originated in the atmosphere-breaks down into 14N. What net change occurred for this to happen? | A. | The 14C lost an electron. | | B. | The 14C gained an electron. | | C. | The 14C lost a proton. | | D. | The 14C gained a proton. | | E. | The 14C gained a neutron. | |
| Blooms Level: 4. Analyze
Chapter - Chapter 02 #14
Learning Outcome: 02.01.03 Describe how variations in an atomic nucleus account for its physical properties.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 15. | What does this graph reveal about the heat of vaporization and the heat of fusion?
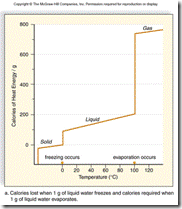 |
| Blooms Level: 6. Create
Chapter - Chapter 02 #15
Learning Outcome: 02.03.03 Analyze how waters solid, liquid, and vapor states allow life to exist on Earth.
Section: 02.03
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 16. | Which of the following statements is NOT true about electron configurations? | A. | If an atom has only one shell, it is complete with two electrons. | | B. | If an atom has two or more shells, the octet rule applies. | | C. | If an atom has two or more shells, the outer shell is complete with eight electrons. | | D. | Atoms with more than eight electrons in the outer shell react by gaining electrons. | | E. | Atoms with eight electrons in the outer shell are not reactive at all. | Incorrect Answers: A. It is true that if an atom has only one shell, it is complete with two electrons. |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #16
Learning Outcome: 02.01.04 Determine how electrons are configured around a nucleus.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 17. | An orbital is best described as | A. | the electron shell closest to the nucleus. | | B. | the outermost electron shell of an atom. | | C. | the volume of space in which electrons are most often found. | | D. | the original energy level of electrons in photosynthesis. | |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #17
Learning Outcome: 02.01.04 Determine how electrons are configured around a nucleus.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 18. | Prior to prescription medications to control stomach acid and "heart burn" people consumed baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) to decrease their discomfort. This would indicate that sodium bicarbonate | A. | effectively buffers stomach acid by releasing H+ | | B. | should be sold as a prescription drug | | C. | blocks acid production by combining with OH- | | D. | neutralizes stomach acid by combining with excess H+ | |
| Blooms Level: 3. Apply
Chapter - Chapter 02 #18
Learning Outcome: 02.04.03 Analyze how buffers prevent large pH changes in solutions.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 19. | Which statement is NOT true about ionic bonds? | A. | One atom acts as an electron donor and another atom acts as an electron acceptor. | | B. | Electrons are completely lost or gained in ion formation. | | C. | An ion has the same number of electrons as a nonionic atom of the same element. | | D. | An ionic bond occurs between positive ions and negative ions. | | E. | A salt such as NaCl is formed by an ionic reaction. | Incorrect Answers: A. It is true that in ionic bonding, one atom acts as an electron donor and another as an electron acceptor. |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #19
Learning Outcome: 02.02.02 List different types of bonds that occur between elements.
Section: 02.02
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 20. | Which statement is NOT true about covalent bonds? | A. | Covalent bonds form when an electron is completely lost or gained from an atom. | | B. | A covalent molecule contains one or more covalent bonds. | | C. | A single covalent bond is drawn as a line between two atoms. | | D. | A pair of electrons is shared between two atoms for each covalent bond. | | E. | Shared electrons allow an atom to complete its outer electron shell in a covalent molecule. | |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #20
Learning Outcome: 02.02.02 List different types of bonds that occur between elements.
Section: 02.02
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 21. | Which statement is NOT true about polar covalent bonds? | A. | Most covalent bonds are nonpolar, with electrons shared fairly equally between the atoms. | | B. | Polar covalent bonds are important in the characteristics of water. | | C. | Electrons are shared unequally in a polar covalent bond. | | D. | The larger atom in a polar bond attracts the electron more strongly than the smaller atom. | | E. | The oxygen of a water molecule is electropositive relative to the hydrogen. | Incorrect Answers: A. It is true that most covalent bonds are nonpolar, with electrons shared fairly equally between the atoms. |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #21
Learning Outcome: 02.02.02 List different types of bonds that occur between elements.
Section: 02.02
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 22. | An abandoned Indiana coal mine spoil bank contains chunks of pyrite minerals. Under constant erosion and weathering, the pyrites leech large amounts of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The spoil banks are also mixed with large quantities of basic limestone and clay carbonates. What should occur over time? | A. | The pH level will drop until all acid has washed out. | | B. | The pH level will remain at 7.0 because of constant washing with rain. | | C. | The pH level will remain at 7.0 because all acid will be immediately neutralized by bases. | | D. | The pH levels will be spotty and vary over time, first more acidic but drifting back toward 7.0. | | E. | Bases always dominate over acids. | |
| Blooms Level: 5. Evaluate
Chapter - Chapter 02 #22
Learning Outcome: 02.04.03 Analyze how buffers prevent large pH changes in solutions.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| | Which of the following statements is/are true about the pH scale? |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02
Learning Outcome: 02.04.01 Identify common acidic and basic substances.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 23. | The scale indicates the relative concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in a solution.
TRUE |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #23
Learning Outcome: 02.04.02 Determine pH from a known H or OH- concentration.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 24. | The scale ranges from 1 to 15.
FALSE |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #24
Learning Outcome: 02.04.01 Identify common acidic and basic substances.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 25. | pH 7 has a balanced level of H+ and OH-.
TRUE |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #25
Learning Outcome: 02.04.01 Identify common acidic and basic substances.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 26. | Anything below pH 7 is acidic and above pH 7 is basic.
TRUE |
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02 #26
Learning Outcome: 02.04.01 Identify common acidic and basic substances.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 27. | A change of one pH unit represents a ten-fold increase or decrease in hydroxyl ion concentration.
TRUE |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #27
Learning Outcome: 02.04.02 Determine pH from a known H or OH- concentration.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 28. | The blood buffer reactions described by H2CO3  H+ + HCO3- indicates that H+ + HCO3- indicates that | A. | scientists are uncertain which direction the equation flows. | | B. | the reaction can flow either direction depending on whether there is an excess of hydrogen or hydroxide ions. | | C. | any reaction in one direction causes an immediate reverse reaction. | | D. | chemicals can swing wildly from acid to basic. | | E. | there is really no difference in chemistry whether a molecule is formed or dissociated. | |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #28
Learning Outcome: 02.04.03 Analyze how buffers prevent large pH changes in solutions.
Section: 02.04
Topic: Chemistry
|
| Blooms Level: 1. Remember
Chapter - Chapter 02
Learning Outcome: 02.02.03 Compare the relative strengths of ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds.
Section: 02.02
Topic: Chemistry
|
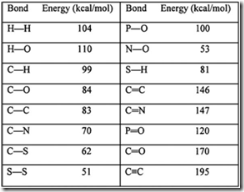
| 29. | From the above table, it is apparent that: | A. | triple bonds are stronger than double bonds; double bonds are stronger than single bonds. | | B. | triple bonds are weaker than double bonds; double bonds are weaker than single bonds. | | C. | carbon bonds are stronger than other bonds; hydrogen bonds are always weakest. | | D. | carbon forms only single bonds. | |
| Blooms Level: 3. Apply
Chapter - Chapter 02 #29
Learning Outcome: 02.02.03 Compare the relative strengths of ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds.
Section: 02.02
Topic: Chemistry
|
| 30. | The characteristic way in which atoms of an element react is most related to the | A. | number of electrons in the outermost shell. | | B. | number of electrons in the innermost shell. | | C. | number of neutrons in the nucleus. | |
| Blooms Level: 2. Understand
Chapter - Chapter 02 #30
Learning Outcome: 02.01.04 Determine how electrons are configured around a nucleus.
Section: 02.01
Topic: Chemistry
|
Virtual Lab: Dependent and Independent Variables
Answer Key
(correct answers are highlighted in red)
- ECB refers to:
- A genetically engineered plant that is resistant to insect pests
- Edible corn byproducts
- An insect pest that reduces corn yield
- European corn borer
- c and d
- How many days are required for a corn seed to become a mature plant with maximum weight kernels ready to be harvested?
- about 23
- about 65
- about 140
- about 180
- “BT Corn” refers to corn that:
- Has been infested with insect pests
- Has been infected with bacteria
- Is resistant to ECB
- Is not affected by pesticides
- BT is:
- A stomach poison produced by bacteria
- A genetically engineered corn product
- A bacterium carried by the European corn borer
- A bacterium that has a gene for producing Cry proteins
- Creation of BT corn requires genetic material from all of the following except:
- European corn borer
- Bacillus thuringiensis
- a corn plant
- all of the above contribute genetic material to the production of BT corn
Table 1: Average Yield for each seed variety at no, low, and high infestation levels
| Seed Variety | Level of ECB Infestation | Pot 1 Yield | Pot 2 Yield | Pot 3 Yield | Average Yield |
| BT 123 | None | 160.1 | 164.8 | 164.2 | 163.0 |
| | Low | 164.0 | 162.6 | 168.3 | 164.9 |
| | High | 155.1 | 163.0 | 163.9 | 160.6 |
| BT 456 | None | 190.0 | 183.2 | 184.8 | 186.0 |
| | Low | 179.6 | 178.8 | 172.6 | 177.0 |
| | High | 157.3 | 157.0 | 159.0 | 157.7 |
| Golden | None | 161.6 | 182.8 | 189.8 | 184.7 |
| | Low | 177.9 | 171.2 | 170.6 | 173.2 |
| | High | 135.4 | 139.6 | 138.3 | 137.7 |
| Super Harvest | None | 164.1 | 164.3 | 161.9 | 163.4 |
| | Low | 159.1 | 155.0 | 157.5 | 157.2 |
| | High | 125.5 | 129.0 | 130.0 | 128.1 |
Table 2: % Reduction in yield for each seed variety at high levels of infestation
(transfer data on average yield with no infestation and high infestation from Table 1 to Table 2)
| Seed Variety | Avg. Yield with No Infestation | Avg. Yield with High Infestation | % Reduction In Yield |
| BT 123 | 163.0 | 160.6 | 1.5% |
| BT 456 | 186.0 | 157.7 | 15.2% |
| Golden | 184.7 | 137.7 | 25.4% |
| Super Harvest | 163.4 | 128.1 | 21.6% |
- For each seed variety, why did you need to collect data from 3 pots for each infestation level to obtain reliable data?
The data from each of the three pots can be used to calculate the average
yield for each seed variety at each infestation level. By using the average yield, the effect of differences in individual seeds and slight variations in conditions on the data can be minimized.
- Which seed variety has the highest yield under conditions of no infestation?
BT 456
- Which transgenic seed variety was most resistant to the ECB at high infestation levels?
BT 123
- Which non-transgenic seed variety was most resistant to the ECB at high infestation levels?
Super Harvest
- Compare the yield of Super Harvest seeds and BT 123 seeds under conditions of no infestation. Is there any difference in the avg. yield?
Yes, although it is very small – only 0.4 g.
- If you compared one pot of Super Harvest and one pot of BT 123 with no infestation, would you expect the yield of each pot to be within 0.4g? Explain your answer.
No, the two yields could be within 0.4g, but these is no way to be sure since this difference in yield represents the difference in the average yield of the two seed varieties, not the actual difference in yield observed between the individual pots.
12. A farmer decides to plant 90% of one field with BT 123 seeds and the remaining 10% of the field with a different seed variety. He hopes this will slow the evolutionary development of BT resistant insects. Which seed variety should he plant in the 10% of his field that is not planted with BT 123 seeds? Explain your answer.
Since he is hoping to slow the development of BT resistant insects, he will
need to plant non-BT seed varieties; this limits his choices to Super
harvest and Golden. Since Golden seeds produce a higher yield under all
conditions, he should plant Golden seeds.

No comments:
Post a Comment