Essential Foundations of Economics, 7/E Robin Bade solutions manual and test bank
Monopoly | Chapter12 | |||||
| ANSWERS TO CHAPTER CHECKPOINTS | ||||||
n Study Plan Problems and Applications
Use the following information to work Problems 1 to 3.
| Price (dollars per bottle) | Quantity | |
| 10 | 0 | |
| 8 | 2,000 | |
| 6 | 4,000 | |
| 4 | 6,000 | |
| 2 | 8,000 | |
| 0 | 10,000 | |
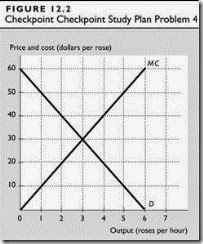
Elixir Spring produces a unique and highly prized mineral water. The firm’s total fixed cost is $5,000 a day, and its marginal cost is zero. The table shows the demand schedule for Elixir water.
1. On a graph, show the demand for Elixir water and Elixir Spring’s marginal revenue curve. What are Elixir’s profit-maximizing price, output, and economic profit?

2. Compare Elixir’s profit maximizing price with the marginal cost of producing the profit-maximizing output. At the profit-maximizing price, is the demand for Elixir water inelastic or elastic?
Elixir’s profit-maximizing price is $5 per bottle and Elixir’s profit-maximizing output is 5,000 bottles per day. The price, $5, is well above the marginal cost, $0. At this price and quantity, the demand for Elixir water is unit elastic because the marginal revenue equals zero.
3. Suppose that there are 1,000 springs, all able to produce this water at zero marginal cost and with zero fixed costs. Compare the equilibrium price and quantity produced with the price and quantity produced by Elixir water.
In this (extreme) situation, the competitive outcome has price equal to marginal cost, $0. The quantity demanded at this price is 10,000 bottles a day, so the equilibrium quantity will be 10,000 bottles a day.
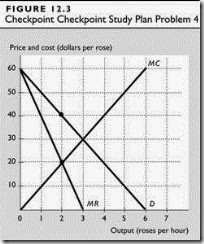
Blue Rose is not using its resources efficiently because Blue Rose is creating a deadweight loss.
Hawaii Cable Television is a natural monopoly. Sketch a market demand curve and the firm’s cost curves. Use your graph to work Problems 5 to 8.

Figure 12.4 illustrates the case of Hawaii Cable when it is unregulated. Hawaii Cable produces the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost, so it serves 20,000 households. The price is $60 a month. The economic profit, consumer surplus, and deadweight loss are illustrated in the figure.
6. If Hawaii Cable is unregulated and it gives householders a 50 percent discount for second and third connections, describe how its economic profit, consumer surplus, and deadweight loss would change.
Hawaii Cable is price discriminating. Its economic profit increases because it will gain additional sales and, presumably, will charge a higher price for the first connection. Consumer surplus decreases as Hawaii Cable charges a higher price. The deadweight loss decreases because the quantity of cable connections increases.

Figure 12.5 illustrates the situation when Hawaii Cable is regulated in the public interest. Hawaii Cable produces the quantity at which the marginal cost curve intersects the demand curve, so it serves 40,000 households. The price is $20 a month. The consumer surplus is the area under the demand curve and above the price, $20 a month. It is equal to the light grey triangle plus the part of the dark rectangle that lies under the demand curve. There is no deadweight loss. There also is no economic profit. Instead, Hawaii Cable incurs an economic loss, shown by the dark grey rectangle.

The price cap will be set at $40 per month. Figure 12.6 shows that with this price cap, Hawaii Cable serves 30,000 households and the price is $40 per month, the same as Hawaii Cable’s average total cost. There is no economic profit. The consumer surplus is equal to the area of the light grey triangle. The deadweight loss is equal to the area of the dark grey triangle.
Use the following information to work Problems 9 and 10.
FCC planning rules to open cable market
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) will make it easier for independent programmers and rival videos services to lease access to cable channels. The FCC will also limit the market share of a cable company to 30 percent.
Source: The New York Times, November 10, 2007
9. What barriers to entry exist in the cable television market? Are high cable prices evidence of monopoly power?
The major barrier to entry is that the cable industry is a natural monopoly. Firms entering the market will have higher average total costs if the amount they produce and sell is less than that of the existing firm. High prices are not necessarily evidence of monopoly. Prices can be high in competitive markets if the costs are high. For instance, the luxury car market is competitive but these cars are quite expensive.
10. Draw a graph to illustrate the effects of the FCC’s new regulations on the price, quantity, consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss.
Presuming that the cable market was an unregulated monopoly before the FCC’s actions and that the market becomes competitive after the actions, Figure 12.7 (on the next page) shows what would happen. With the 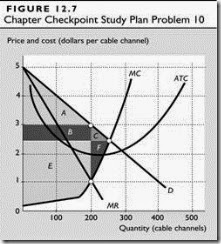
11. Read Eye on Microsoft on p. 331 and explain how Window’s price, quantity, consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss would change if Microsoft was able to sell ads that appear every time a user opens a program. Illustrate your answer with a graph.

n Instructor Assignable Problems and Applications
Use the following information to work Problems 1 and 2.
Microsoft: We're not gouging Europe on Windows 7 pricing
Regulators in the European Union have charged Microsoft with illegally tying Internet Explorer (IE) to Windows and mandated that a version of Windows be offered stripped of IE. A news report suggested that when Microsoft launches Windows 7, it will charge a higher price for the IE-stripped version than the price for a full version that includes IE. Microsoft denied this report but announced that it would offer the full version of Windows 7 at a lower upgrade price.
Source: computerworld.com
1. How does Microsoft set the price of Windows and would it be in the firm’s self-interest to set a different price for a version stripped of IE?
Microsoft sets the price of Windows at the amount that maximizes its profit. Stripping IE increases Microsoft’s fixed costs but has no effect on its variable cost or its marginal cost. Microsoft will set different prices if the marginal revenue of the two Windows versions are different.
2. Why might Microsoft offer the full version of Windows 7 to European customers at a lower upgrade price?
Stripping IE increases Microsoft’s costs. Microsoft might set a lower price—the upgrade price—for the full version of Windows 7 than for the stripped version because Microsoft’s cost of the full version is less than its cost for the stripped version.
Use the following information to work Problems 3 and 4.
| Price | Quantity | Marginal cost |
| 20 | 0 | - |
| 18 | 1 | 1 |
| 16 | 2 | 4 |
| 14 | 3 | 8 |
| 12 | 4 | 12 |
| 10 | 5 | 18 |
Bobbie’s Hair Care is a natural monopoly. The table shows the demand schedule (the first two columns) and Bobbie’s marginal cost schedule (the middle and third columns). Bobbie has done a survey and discovered that she has four types of customers each hour: one woman who is willing to pay $18, one senior who is willing to pay $16, one student who is willing to pay $14, and one boy who is willing to pay $12. Suppose that Bobbie’s fixed costs are $20 an hour and Bobbie’s price discriminates.
3. What is the price each type of customer is charged and how many haircuts an hour does Bobbie’s sell? What is the increase in Bobbie’s economic profit that results from price discrimination?
If Bobbie price discriminates, she charges the woman $18, the senior citizen $16, the student $14, and the boy $12. If Bobbie price discriminates, she sells 4 haircuts an hour. Bobbie’s economic profit is her total revenue minus her total cost. If she does not price discriminate, she produces the quantity such that marginal revenue equals marginal cost. Bobbie’s marginal revenue when she produces 3 haircuts is equal to her marginal cost when she produces 3 haircuts. (Both are equal to $8.) So without price discrimination, Bobbie’s produces 3 haircuts an hour at a price of $14. In this case, her economic profit is her total revenue, $42, minus her total cost, $33 (the sum of the fixed cost plus the marginal costs), which is $9. If she price discriminates, her total revenue is $18 + $16 +$14 + $12, which is $60. Her total cost to produce 4 haircuts is $45, so her economic profit is $60 - $45, which is $15. So her economic profit increases by $6.
4. Who benefits from Bobbie’s price discrimination? Is the quantity of haircuts efficient?
When Bobbie price discriminates, Bobbie benefits because her economic profit is higher. Because Bobbie is perfectly price discriminating, Bobbie is producing the efficient quantity of haircuts. With price discrimination, the boy willing to pay $12 benefits because he now gets a haircut. Society benefits because the deadweight loss is eliminated.
Use the following information to work Problems 5 through 10.
| Price | Quantity | Total cost | ||
| 20 | 0 | 1,000 | ||
| 18 | 100 | 1,600 | ||
| 16 | 200 | 2,200 | ||
| 14 | 300 | 2,800 | ||
| 12 | 400 | 3,400 | ||
| 10 | 500 | 4,000 | ||
| 8 | 600 | 4,600 | ||
| 6 | 700 | 5,200 | ||
| 4 | 800 | 5,800 | ||
Big Top is the only circus in the nation. The table sets out the demand schedule for circus tickets and the cost schedule for producing the circus.
5. Calculate Big Top’s profit-maximizing price, output, and economic profit if it charges a single price for all tickets.
Big Top’s total revenue and marginal revenue schedules are in the second table (on the next page), which is useful to answer these questions. Big Top’s marginal cost is constant and equal to $6 per ticket. Big Top’s marginal revenue equals its marginal cost when the quantity of tickets is 350 tickets per show and the price is $13 per ticket. The total revenue is 350 tickets ´ $13, which is $4,550. The total cost of 350 tickets is $3,100. So the economic profit equals $4,550 - $3,100, which is $1, 450.
6. When Big Top maximizes profit, what is the consumer surplus and producer surplus and is the circus efficient? Explain why or why not.
The consumer surplus equals the triangular area under the demand curve and above the price. The height of this triangle is the price at which the quantity demanded is zero ($20) minus the equilibrium price and the base of the triangle is the equilibrium quantity. The consumer surplus equals
| Price | Quantity | Total | Marginal |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | |
| 18 | 100 | 1800 | 18 |
| 16 | 200 | 3200 | 14 |
| 14 | 300 | 4200 | 10 |
| 12 | 400 | 4800 | 6 |
| 10 | 500 | 5000 | 2 |
| 8 | 600 | 4800 | -2 |
| 6 | 700 | 4200 | -6 |
| 4 | 800 | 3200 | -10 |
1/2 ´ ($20 - $13) ´ 350, which is $1,225. The producer surplus is the area above the marginal cost curve and below the price. Because the marginal cost curve is horizontal, this area is a rectangle equal to ($13 - $6) ´ 350, which is $2,450. When Big Top maximizes its profit, the circus is not efficient. At 350 tickets, the marginal cost of another ticket is $6 and the marginal benefit from another ticket (which is equal to the maximum a consumer is willing to pay) is $13. Marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost, so a deadweight loss exists.
7. At the market equilibrium, no children under 10 years old attend the circus. Big Top offers children under 10 a discount of 50 percent. How will this discount change the consumer surplus and producer surplus? Will Big Top be more efficient by offering the discount to children?
If Big Top offers a child discount, the consumer surplus increases because more children attend. Presumably the producer surplus increases (as Big Top’s production increases) because Big Top would be unwilling to offer a discount otherwise. Big Top sells more tickets and so it operates closer to the efficient level of output but it is unlikely to produce the efficient quantity.
8. If Big Top is regulated to produce the efficient output, what is the quantity of tickets sold, what is the price of a ticket, and what would be the consumer surplus?
Big Top’s marginal cost is constant at $6 per ticket. To operate efficiently Big Top’s marginal cost must equal the price, so the price of a ticket is $6. At this price, the quantity of tickets sold will be 700 tickets per show. The consumer surplus equals 1/2 ´ ($20 - $6) ´ 700, which is $4,900.
9. If Big Top is regulated to charge a price equal to average total cost, what is the quantity of tickets sold, the price of a ticket, and economic profit?
The quantity will be a bit more than 600 and the price will somewhat less than $8. Because the price equals the average total cost, the economic profit is zero. (Interpolation of the total cost and demand schedules shows that the “precise” quantity is 619 tickets and the “precise” price is $7.62. At this quantity, interpolation of the total cost schedule is $4,716 and so the average total cost is $7.62, equal to the price).

Figure 12.9 shows the situation if regulators set a price cap that allows Big Cap to break even. The price cap is a touch under $8 because this is the price at which the average total cost curve intersects the demand curve. The quantity of tickets sold is a bit more than 600. The deadweight loss is equal to the area of the grey triangle.
n Multiple Choice Quiz
1. A firm is a natural monopoly if ________.
A. it can produce the good at a price below its competitor’s price
B. it can produce a larger quantity of the good than other firms could
C. the government grants it a public franchise or patent
D. it can satisfy the market demand at a lower average total cost than other firms can
Answer: D Answer D is the definition of a natural monopoly.
2. A monopoly ________.
A. can choose its price and output and always has the option of price discriminating
B. is a price taker and by offering a range of discounts can price discriminate
C. that produces a good that cannot be resold might choose to price discriminate
D. book store that offers a discount on Tuesdays is price discriminating
Answer: C The monopoly has the potential of price discriminating only when the good cannot be resold.
3. A single-price monopoly maximizes profit by producing the quantity at which _____.
A. its total revenue will be as large as possible
B. marginal revenue equals marginal cost and setting the price equal to marginal revenue
C. marginal revenue equals marginal cost and setting the price equal to marginal cost
D. marginal revenue equals marginal cost and setting the price equal to the most people are willing to pay for that quantity
Answer: D Figure 12.4(b) illustrates that answer D is correct.
4. A monopoly sets its price such that demand for the good produced is ______.
A. unit elastic
B. inelastic
C. elastic
D. either elastic or inelastic, but never unit elastic
Answer: C To maximize profit, marginal cost must equal marginal revenue. Marginal cost is positive, so to maximize profit marginal revenue must also be positive. Only when the demand is elastic is marginal revenue positive.
5. A single-price monopoly is ______.
A. inefficient because it converts consumer surplus to producer surplus
B. inefficient because it produces too small an output and creates a deadweight loss
C. efficient because buyers are paying a price equal to their willingness to pay
D. efficient because it is the only producer of the good
Answer: B The monopoly creates inefficiency by producing less than a competitive market to raise its price.
6. A monopoly that price discriminates ______.
A. benefits buyers because it offers the good at a variety of prices
B. gains because it converts consumer surplus to economic profit
C. uses resources more efficiently than would a competitive market
D. enables buyers to maximize their consumer surplus
Answer: B Price discrimination converts consumer surplus to economic profit.
7. Governments regulate natural monopoly by capping the price at _____.
A. marginal revenue and allowing the monopoly to maximize profit
B. marginal cost so that the monopoly is efficient and makes zero economic profit
C. average total cost, which allows the monopoly to be inefficient but make zero economic profit
D. the buyers’ willingness to pay, which makes the monopoly operate efficiently
Answer: C Figure 12.12 illustrates the effects of using an average cost pricing rule to regulate the natural monopoly.
Foundations of Macroeconomics, 7e (Bade/Parkin)
Chapter 9 Economic Growth
9.1 The Basics of Economic Growth
1) Economic growth is defined as
A) a decrease in the rate of inflation.
B) an increase in employment.
C) a sustained expansion of production possibilities.
D) an increase in the wage rate.
E) an increase in the nation's population.
Answer: C
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
2) Economic growth is a sustained expansion of production possibilities, as measured by the increase in ________ over time.
A) real GDP
B) population
C) inflation
D) the price level
E) employment
Answer: A
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
3) A country will likely experience an increase in poverty if
A) its population decreases over time.
B) its real GDP growth rate decreases or slows over time.
C) its inflation rate decreases or slows over time.
D) its real GDP per person growth rate increases over time.
E) it does not receive foreign aid.
Answer: B
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
4) Economic growth is defined as equal to the increase in
A) employment.
B) population.
C) real GDP.
D) the price level.
E) the inflation rate.
Answer: C
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
5) Which of the following variables is used to determine a country's economic growth?
i. real GDP
ii. wages
iii. inflation
A) i and ii only
B) i, ii and iii
C) ii and iii
D) i only
E) i and iii
Answer: D
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
6) The growth rate of real GDP equals
A) [(employment in the current year - employment in previous year)/employment in previous year] × 100.
B) [(real GDP in current year - real GDP in previous year) ÷ real GDP in previous year] × 100.
C) [(real GDP in previous year - real GDP in current year) ÷ real GDP in previous year] × 100.
D) [(real GDP in current year - real GDP in previous year) ÷ real GDP in current year] × 100.
E) (real GDP in current year - real GDP in previous year) × 100.
Answer: B
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
7) If real GDP was $13.1 trillion in 2013 and $13.3 in 2014, what is the growth rate?
A) 15.0 percent
B) -1.5 percent
C) 1.5 percent
D) $0.2 trillion
E) 2.1 percent
Answer: C
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
8) Suppose France's real GDP grew from $750 billion in 2010 to $821 billion in 2011. What was the growth rate of France's real GDP?
A) 10 percent
B) 9.5 percent
C) 9.1 percent
D) 8.6 percent
E) $71 billion
Answer: B
Topic: Growth rate
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
9) U.S. real GDP in 2007 was $13.25 trillion and U.S. real GDP in 2008 was $13.31 trillion. What was the economic growth rate of the United States during this period?
A) 18 percent
B) -1.36 percent
C) 0.45 percent
D) 6.9 percent
E) $1.8 trillion
Answer: C
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Revised
AACSB: Analytical thinking
10) If real GDP in year 1 is $72 million and real GDP in year 2 is $87 million, then the growth rate of real GDP is
A) 15 percent.
B) $15 million.
C) 20.8 percent.
D) 17 percent.
E) 83 percent.
Answer: C
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
11) In 2008, real GDP in the United States was $13,312 billion. In 2009, real GDP in the United States was $13,112 billion. What was the U.S. economic growth rate from 2008 to 2009?
A) -1.5 percent
B) 1.5 percent
C) 0.98 percent
D) 0.12 percent
E) $200 million
Answer: A
Topic: Growth rate
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
12) Using the data in the table above, the growth rate of real GDP for 2010 is equal to
A) 9.09 percent.
B) 7.00 percent.
C) 5.00 percent.
D) 4.76 percent.
E) 10.0 percent.
Answer: B
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
13) Using the data in the table above, real GDP per person in 2009 is
A) $70,000.
B) $71,429.
C) $75,000.
D) $70 trillion.
E) 7 percent.
Answer: A
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
14) Using the data in the table above, the growth rate of real GDP has
A) increased from year to year.
B) increased more rapidly from year to year.
C) remained constant from year to year.
D) slowed from year to year.
E) probably changed, but more information is needed about the price level to determine by how much it has changed.
Answer: A
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
15) Suppose India wants to measure how much the standard of living has changed over the last decade. Which piece of data should India use?
A) population
B) real GDP per person
C) real GDP
D) wages
E) inflation
Answer: B
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
16) To measure the change in the standard of living, it is best to use the growth rate
A) from the Rule of 70.
B) of real GDP.
C) of the population.
D) of real GDP per person.
E) of the price level.
Answer: D
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
17) In growth theory, the change in a country's standard of living is measured by the change in
A) real GDP per person.
B) real GDP.
C) the nation's capital stock.
D) wages per person.
E) employment.
Answer: A
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
18) A measure of growth in the standard of living is the growth in
A) real GDP.
B) population.
C) real GDP minus the growth in population.
D) population minus the growth in real GDP.
E) employment.
Answer: C
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
19) Growth in the standard of living is measured by the increase in
A) real GDP.
B) the Rule of 70.
C) employment.
D) real GDP per person.
E) consumption.
Answer: D
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
20) The growth rate of real GDP per person equals the
A) population growth rate plus the growth rate of real GDP.
B) change in the economic growth rate divided by the change in the population growth rate.
C) the economic growth rate per person divided by the change in the population growth rate.
D) growth rate of real GDP minus the growth rate of the population.
E) population growth rate plus the growth rate of real GDP then divided by the initial level of real GDP.
Answer: D
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
21) If real GDP grows at a faster rate than does population, then the standard of living, as measured by real GDP per person,
A) improves.
B) worsens.
C) remains the same.
D) cannot be measured.
E) either improves, worsens, or stays the same, depending on the size of the population and the actual level of real GDP.
Answer: A
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
22) The population in the current year is 31.5 million and the real GDP is $814 million. The previous year's statistics were a population of 31 million and a real GDP of $800 million. The change in the standard of living, measured by growth in real GDP per person, is
A) 1.6 percent.
B) 7.75 percent.
C) 0.13 percent.
D) 6 percent.
E) 0 percent.
Answer: C
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
23) Assume the population growth rate is 2 percent and the real GDP growth rate is 5 percent. The change in standard of living, as measured by the growth rate in real GDP per person, is
A) 7 percent.
B) 2.5 percent.
C) 5 percent.
D) 3 percent.
E) -3 percent.
Answer: D
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
24) Real GDP in the country of Oz is growing at 5 percent and its population is growing at 2 percent. In the country of Lilliput, real GDP is growing at 4 percent and its population is growing at 0.5 percent. Thus,
A) real GDP per person in Oz is growing at a faster rate than in Lilliput.
B) real GDP per person in Lilliput is growing at a faster rate than in Oz.
C) real GDP per person in Lilliput is growing at the same rate as in Oz.
D) real GDP per person in Lilliput is growing at a rate that is not comparable to that in Oz.
E) We need more information to determine if real GDP per person in Lilliput is growing faster or slower than real GDP per person in Oz.
Answer: B
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
25) If the U.S. population grew at a 0.9 percent and real GDP grew at a 4.4 percent during the same period, what was the growth rate of real GDP per person?
A) 3.5 percent
B) 5.3 percent
C) 4.0 percent
D) -3.5 percent
E) 4.4 percent
Answer: A
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
26) If real GDP grows at a rate of 6 percent and population grows at a rate of 2 percent, then real GDP per person grows at a rate of
A) 4 percent.
B) 2 percent.
C) 0.5 percent.
D) -3 percent.
E) 8 percent.
Answer: A
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
27) Iceland's real GDP grows at a rate of 2.6 percent and population grows at a rate of 0.8 percent. Iceland's real GDP per person grows at a rate of
A) 1.8 percent.
B) 2.6 percent.
C) 3.4 percent.
D) 3.0 percent.
E) 3.2 percent.
Answer: A
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
28) If an economy's growth rate of real GDP is 3 percent per year and the growth rate of the population is 2.5 percent per year, the growth rate of real GDP per person is
A) 3 + 2.5 = 5.5 percent per year.
B) [(3 - 2.5) ÷ 2.5] × 100 = 20 percent per year.
C) [(2.5 - 3) ÷ 3] × 100 = 16.6 percent per year.
D) 3 - 2.5 = 0.5 percent per year.
E) 2.5 - 3 = -0.5 percent per year.
Answer: D
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
29) In 2009, U.S. real GDP decreased by 3 percent and the population grew by 1 percent. Thus, real GDP per person
A) increased 2 percent.
B) decreased 2 percent.
C) increased 4 percent.
D) decreased 4 percent.
E) decreased 3 percent.
Answer: D
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
30) If a country experiences a real GDP growth rate of 1 percent and population growth of 2 percent, then the growth rate of real GDP per person is
A) 3 percent.
B) 2 percent.
C) 1 percent.
D) -1 percent.
E) 0 percent.
Answer: D
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
31) During 2008, Swaziland had a real GDP growth rate of 1.8 percent and a real GDP growth rate per person of -1.3 percent. These rates indicate that in Swaziland
A) there was an error when calculating the growth rates because the growth rate of real GDP per person cannot be negative.
B) the population growth rate was negative.
C) the population grew at a faster rate than real GDP.
D) poverty levels are declining.
E) real GDP grew more rapidly than did the population.
Answer: C
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 5: Critical thinking
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
32) In India last year, the growth rate of real GDP was 3.5 percent and the population grew from 1,000 million people to 1,100 million. Real GDP per person
A) increased by 13.5 percent.
B) decreased by 6.5 percent.
C) increased by 6.5 percent.
D) decreased by 13.5 percent.
E) increased by 3.5 percent.
Answer: B
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
33) Belgium's real GDP per person is $33,000 and Austria's is $34,700. The population growth rate in Belgium is 0.13 percent and the growth rate of real GDP is 3.0 percent. The population growth rate in Austria is 0.08 percent and the growth rate of real GDP is 3.3 percent. If these growth rates continue, how many years will it take for Belgium's real GDP per person to equal Austria's real GDP per person?
A) Belgium's standard of living will never equal Austria's.
B) just over 23 years
C) just over 24 years
D) just over 21 years
E) over 230 years
Answer: A
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
34) If Country A's real GDP is growing at 6 percent per year and Country B's real GDP is growing at 6 percent per year, then the standard of living is
A) growing more rapidly in Country A.
B) higher in Country B.
C) changing at the same rate in Country A and Country B.
D) growing more slowly in Country A.
E) changing at the same rate in Country A and Country B only if the rate of population growth is the same in both countries.
Answer: E
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
35) If Country A's real GDP per person is growing at 6 percent and Country B's real GDP per person is growing at 3 percent, then
A) the standard of living is higher in Country A.
B) the standard of living is higher in Country B.
C) the standard of living is growing more rapidly in Country A.
D) We cannot say whose standard of living is growing more rapidly without knowing the population growth rate.
E) We cannot say whose standard of living is growing more rapidly without knowing the growth rate of real GDP.
Answer: C
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
36) According to the data in the table above,
A) the standard of living improved between year 1 and year 2.
B) the standard of living worsened between year 1 and year 2.
C) as measured by real GDP per person, the standard of living remained the same between year 1 and year 2.
D) real GDP grew more rapidly than population between year 1 and year 2.
E) real GDP grew more slowly than population between year 1 and year 2.
Answer: C
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
37) According to the data in the table above, real GDP grew at a rate of ________ between year 1
and year 2.
A) 10 percent
B) 1 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 5 percent
E) 55 percent
Answer: A
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
38) According to the data in the table above, real GDP per person grew at a rate of ________ between year 1 and year 2.
A) 10 percent
B) 0 percent
C) 1 percent
D) 5 percent
E) 50 percent
Answer: B
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
39) The Rule of ________ can be used to calculate the number of years that it takes for the level of a variable to ________.
A) 20; double
B) 70; triple
C) 70; double
D) 20; triple
E) thumb; double
Answer: C
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
40) The Rule of 70 states that the level of a variable will double in
A) 70 years.
B) the number of years equal to the variable's annual rate of growth divided by 70.
C) the number of years equal to 70 divided by the variable's annual growth rate.
D) the number of years equal to the variable's annual growth rate minus 70.
E) the number of years equal to 70 multiplied by the variable's annual growth rate expressed as a decimal.
Answer: C
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
41) The Rule of 70, as applied to real GDP growth, can be used to find the
A) real GDP growth rate necessary to double growth.
B) number of years it takes for the level of real GDP to double.
C) growth rate of real GDP.
D) number of years it takes for the growth rate of real GDP to double.
E) population growth rate necessary to double the GDP growth rate.
Answer: B
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
42) The Rule of 70 can be used to calculate the
A) economic growth rate per month.
B) population growth rate per year.
C) number of years it would take for the level of any variable to double.
D) 70 percent level of the economic growth rate.
E) economic growth rate per year.
Answer: C
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
43) Approximately how long will it take Ethiopia to double its real GDP per person of $100 if its growth rate of real GDP per person is 0.9 percent?
A) 63 years
B) 77.7 years
C) 70 years
D) 109 years
E) 100 years
Answer: B
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
44) If Country A's real GDP grows at a rate of 14 percent per year, about how many years will it take for Country A's real GDP to double?
A) 10
B) 7
C) 5
D) 30
E) 14
Answer: C
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
45) According to the Rule of 70, if a country grows at 2.0 percent per year instead of 1.5 percent per year, how many fewer years will it take to double its level of real GDP?
A) It will take 11.6 years fewer.
B) It will take 35 years fewer.
C) It will take 58.3 years fewer.
D) It will take 20 years fewer.
E) It will take 17.9 years fewer.
Answer: A
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
46) The annual growth rate of an economy is 10 percent. The economy's GDP will double in about ________ years.
A) 7
B) 10
C) 12
D) 14
E) 20
Answer: A
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
47) Using the rule of 70, a sustained 3 percent per year real GDP growth rate will
A) last for 70 years.
B) double the current level of real GDP in about 23 years.
C) double the current level of real GDP in about 210 years.
D) double the current level of real GDP in about 70 years.
E) double the current level of real GDP in about 40 years.
Answer: B
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
48) A nation's annual growth rate of real GDP per person is 2 percent. Its standard of living will
A) double in 35 years.
B) not change because its population is growing.
C) fall because of its population growth.
D) double in 10 years.
E) double in 50 years.
Answer: A
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
49) If a country experiences a real GDP growth rate of 6 percent, real GDP will double in
A) 10 years.
B) 11.67 years.
C) 14 years.
D) 17.5 years.
E) 16.67 years.
Answer: B
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
50) This year, real GDP per person in Country A is eight times real GDP per person in Country B. If Country B's real GDP per person grows at a rate of 5 percent, about how many years will it take for Country B to reach the level of real GDP per person in Country A in this year?
A) 14 years
B) 28 years
C) 56 years
D) 42 years
E) It will never reach Country A's level of GDP per person.
Answer: D
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
51) This year Iceland has a real GDP per person that is approximately 8 times greater than that of Cape Verde. Cape Verde's growth rate of real GDP per person was 5.2 percent. If Cape Verde maintains this current growth rate, approximately how many years will it take for Cape Verde's real GDP per person to reach the same level that Iceland has this year?
A) 13.5 years
B) 20 years
C) 27 years
D) 40 years
E) 54 years
Answer: D
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
52) If it took 20 years for real GDP to double, what was the growth rate of real GDP?
A) 4.5 percent
B) 3.0 percent
C) 3.5 percent
D) 4 percent
E) 5 percent
Answer: C
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
53) In this year, Country A has a real GDP per person that is 4 times greater than that of Country B. Country B's growth rate of real GDP per person is 3.5 percent per year. How many years will it take for Country B's real GDP per person to reach the same level that Country A had in this year?
A) 10 years
B) 20 years
C) 40 years
D) 60 years
E) 56 years
Answer: C
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
54) Suppose Mexico's real GDP per person in 2008 is $6,000 and the U.S. real GDP per person is $24,000. Mexico has annual growth in real GDP per person of 5 percent. Approximately how many years will it take Mexico to equal $24,000 of real GDP per person?
A) 14 years
B) 18 years
C) 28 years
D) 36 years
E) 40 years
Answer: C
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
55) Over the past 110 years, real GDP per person in the United States has grown at an average rate of about ________ per year.
A) 1 percent
B) 2 percent
C) 5 percent
D) 10 percent
E) 7.5 percent
Answer: B
Topic: Eye on the past, how fast has real GDP per person grown?
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Revised
AACSB: Reflective thinking
56) For the world, what period of time experienced the fastest growth rate of real GDP per person?
A) around 500 B.C.
B) around 400 A.D.
C) between 1000 A.D. and 1500 A.D.
D) after about 1850 A.D.
E) between 1500 A.D. and 1850 A.D.
Answer: D
Topic: Eye on the past, how fast has real GDP per person grown?
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
57) Real GDP per person averaged $150 a year (in 2009 dollars) from 1,000,000 BC until 1620. During this time there was a period when it rose to ________ around ________ because ________.
A) $210; 1620; the Pilgrim Fathers began to arrive in the Americas
B) $210; 1492; Columbus sailed to the Americas
C) $140; 400 BC; the Roman Empire collapsed
D) $190; 500 BC; of the gains from human capital while Aristotle and Plato were teaching in Athens
E) a 1-million year high; the 1340s; the Black Death gripped Europe
Answer: D
Topic: Eye on the past, how fast has real GDP per person grown?
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
58) Real GDP per person averaged $150 a year (in 2009 dollars) from 1,000,000 BC until 1620. Then in ________ real GDP began to increase without limit and by 1850 had risen to twice its 1650 level because ________.
A) 1650; the Pilgrims arrived in the Americas
B) 1750; Columbus arrived in the Americas
C) 1650; of the Industrial Revolution
D) 1750; of the Industrial Revolution
E) 1776; United States was founded
Answer: D
Topic: Eye on the past, how fast has real GDP per person grown?
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
59) Since the beginning of the 20th century the decade with the slowest real GDP per person growth rate other than the 1930s is ________ because of the ________.
A) 2000-2010; the war on terror
B) 1990-2000; fear of Y2K
C) 1930-1940; Great Depression
D) 2000-2010; 2008/2009 deep recession
E) 2010-2020; Keynesian economic policies being used more frequently than in the 1930s
Answer: D
Topic: Eye on the past, how fast has real GDP per person grown?
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
60) The economic growth rate is measured as the
A) annual percentage change of real GDP.
B) annual percentage change of employment.
C) amount of real GDP.
D) annual percentage change of the population.
E) amount of population.
Answer: A
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
61) Economic growth is a sustained expansion of production possibilities measured as the increase in ________ over a given period.
A) real GDP
B) real GDP per person
C) the standard of living
D) capital per person
E) population
Answer: A
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
62) The economic growth rate is expressed as the
A) annual percentage change of real GDP per person.
B) growth rate of real GDP minus the growth rate of population.
C) standard of living.
D) annual percentage change of real GDP.
E) growth rate of the population.
Answer: D
Topic: Economic growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
63) Real GDP is $9 trillion in the current year and $8.6 trillion in the previous year. The economic growth rate between these years has been
A) 10.31 percent.
B) 4.65 percent.
C) 5.67 percent.
D) 7.67 percent.
E) $0.4 trillion.
Answer: B
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
64) The table gives information about the economy of Japan. The economic growth rate in 1997 is ________ percent.
A) 8.0
B) 0.8
C) 0.08
D) 0.008
E) 4
Answer: B
Topic: Calculating growth rates
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
65) The standard of living is measured by
A) real GDP.
B) employment.
C) employment per person.
D) real GDP per person.
E) the population.
Answer: D
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
66) If the growth rate of population is greater than a nation's growth rate of real GDP, then its real GDP per person
A) falls.
B) rises.
C) does not change.
D) might rise, fall, or not change.
E) cannot be measured.
Answer: A
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
67) The table above gives information about the economy of France. The growth rate of real GDP per person in 1998 is ________ percent.
A) 3.1
B) 0.4
C) 3.6
D) 4.0
E) 1.9
Answer: C
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Revised
AACSB: Analytical thinking
68) If real GDP increases by 6 percent and at the same time the population increases by 2 percent, then real GDP per person grows by
A) 6 percent.
B) 4 percent.
C) 2 percent.
D) 8 percent.
E) 3 percent.
Answer: B
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
69) If real GDP grew 5 percent last year and the population grew 2 percent, then real GDP per person grew by ________ percent.
A) 10
B) 5
C) 3
D) 2
E) 7
Answer: C
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
70) If a country experiences a real GDP growth rate of 4 percent, real GDP will double in
A) 14 years.
B) 17.5 years.
C) 23.3 years.
D) 35 years.
E) 25 years.
Answer: B
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
71) Suppose that in the future, real GDP per person grows 2 percent a year in the United States and 4 percent a year in China. It will take real GDP per person approximately ________ years to double in the United States and approximately ________ years to double in China.
A) 70; 35
B) 35; 17.5
C) 35; 8.75
D) 50; 25
E) 20; 10
Answer: B
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
72) The table above gives information about the economy of Spain. If the growth rate in 1998 is maintained, real GDP will double in ________ years.
A) 4
B) 19
C) 10
D) 18
E) 25
Answer: D
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
9.2 Labor Productivity Growth
1) Labor productivity is defined as
A) total real GDP.
B) real GDP per person.
C) total output multiplied by total hours of labor.
D) real GDP per hour of labor.
E) hours of work per person.
Answer: D
Topic: Sources of growth, labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
2) Labor productivity equals
A) real GDP.
B) real GDP per hour of labor.
C) the total production of labor.
D) the quantity of labor hours divided by real GDP.
E) real GDP divided by the amount of human capital.
Answer: B
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
3) Labor productivity is equal to the quantity of
A) real GDP produced by one hour of labor.
B) workers employed during one hour.
C) real GDP consumed by the total population in one hour.
D) real GDP.
E) workers who are gainfully employed.
Answer: A
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
4) The quantity of real GDP produced by one hour of labor is defined as
A) real GDP per person.
B) the advance in technology.
C) the growth rate of technology.
D) labor productivity.
E) economic growth.
Answer: D
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
5) Labor productivity is calculated as
A) (real GDP ÷ aggregate hours).
B) (real GDP ÷ aggregate hours × number of workers).
C) (real GDP ÷ number of workers × ratio of capital per worker).
D) (real GDP ÷ technology level).
E) (real GDP ÷ aggregate hours × number of workers) × 100.
Answer: A
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
6) Sustained increases in the standard of living depend on
A) increases in the quantity of labor.
B) increases in the population.
C) increases in aggregate hours.
D) increases in labor productivity.
E) decreases in labor productivity.
Answer: D
Topic: Sources of growth, labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
7) An increase in labor productivity
A) increases the standard of living.
B) decreases the standard of living.
C) might be the result of an increase in the quantity of labor.
D) generally occurs when physical capital decreases because firms must then hire more workers.
E) cannot occur without a corresponding increase in employment.
Answer: A
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
8) Last year, in a nation far to the South, real GDP was $90 million and 900,000 workers were employed. This year real GDP is $100 million, 950,000 workers are employed, and the number of hours each worker works per year did not change. Hence, labor productivity
A) has increased.
B) has decreased.
C) has remained constant.
D) cannot be compared between the two years because both real GDP and the number of workers increased.
E) might have changed, but more information is needed to determine if it changed.
Answer: A
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
9) If real GDP is $6,460 billion, the population is 184.6 million people, and aggregate hours is 170 billion hours, labor productivity is
A) $2.63 an hour.
B) $2.86 an hour.
C) $35,000.
D) $38.00 an hour.
E) 920 hours.
Answer: D
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
10) Real GDP is $700 billion, average hours worked per week is 42 and aggregate hours is 150 billion hours. What is the economy's labor productivity?
A) $1.80 per hour
B) $3.75 per hour
C) $16.67 per hour
D) $4.67 per hour
E) $4.50 per hour
Answer: D
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Revised
AACSB: Analytical thinking
11) Labor productivity growth depends on
i. saving and investment.
ii. increases in human capital.
iii. technological growth.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) Both ii and iii
E) i, ii, and iii
Answer: E
Topic: Increase in labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
12) Labor force productivity has increased from $30 per hour to $32 per hour over the past year. This could result from
A) only an increase in real GDP.
B) an increase in real GDP with no change in the aggregate hours or a decrease in aggregate hours with no change in real GDP.
C) only a decrease in aggregate hours.
D) an increase in the labor force participation rate.
E) an increase in population.
Answer: B
Topic: Increase in labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
13) In recent years, Taiwan has experienced increases in savings and investment. As a result of the higher investment and saving, we expect
i. increases in physical capital.
ii. increases in the inflation rate.
iii. advances in technology.
A) i and iii
B) i and ii
C) ii only
D) ii and iii
E) i, ii and iii
Answer: A
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, physical capital
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
14) If the stock of physical capital (that is machinery, equipment, etc.) and human capital remains the same and the population increases, then
A) labor productivity will increase.
B) labor productivity will decrease.
C) the standard of living will increase.
D) the new labor will be more productive.
E) real GDP decreases.
Answer: B
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, physical capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
15) The widespread adoption of computers in the workplace has likely led to
A) no change in the quantity of labor hours.
B) an increase in labor productivity because computers are a capital good.
C) a decrease in labor productivity because computers are a capital good.
D) a decrease in human capital because computers are physical capital.
E) an increase in the supply of labor because people are needed to operate the computers.
Answer: B
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, physical capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
16) An increase in capital brings a large increase in output at a ________ quantity of capital and a small increase in output at a ________ quantity of capital because of ________.
A) small; large; increasing returns along the productivity curve
B) small; large; diminishing returns along the productivity curve
C) large; small; diminishing returns along the productivity curve
D) large; small; increasing returns along the productivity curve
E) large; small; the greater the quantity of capital the greater the output
Answer: B
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, physical capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
17) Which of the following are required for economic growth?
i. more goods and services produced per hour of work
ii. an increase in the average hours of labor per person
iii. an increase in prices
A) i and iii
B) i and ii
C) ii and iii
D) i only
E) ii only
Answer: B
Topic: Increase in labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
18) A reason for an increase in labor productivity growth is
A) an increase in people's human capital.
B) a decrease in the capital stock so that firms must hire more workers.
C) growth in the supply of labor.
D) an increase in the population so that firms hire more workers.
E) an increase in the quantity of labor.
Answer: A
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
19) Human capital refers to the
A) accumulated skill and knowledge of human beings.
B) accumulated equipment used by human beings.
C) accumulation of money by human beings.
D) accumulation of money and equipment used by human beings.
E) accumulated financial capital people have acquired.
Answer: A
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
20) Human capital is defined as the
A) amount of machinery human beings have.
B) number of factories built for human beings.
C) accumulated skill and knowledge of human beings.
D) accumulated amount of machinery and factories human beings own.
E) skills that people are born with.
Answer: C
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
21) Increases in human capital can come
A) only from formal schooling.
B) from employing more machinery.
C) only from on-the-job experience.
D) from formal education and on-the-job learning.
E) from nowhere because whatever human capital an individual possesses is what he or she was born with.
Answer: D
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
22) Expansion of a nation's human capital can be achieved through
A) education and training.
B) education and saving.
C) education and technology improvements.
D) education only.
E) nothing because human capital is determined by the skills people are born with.
Answer: A
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
23) Human capital is acquired
A) only in school.
B) only through on-the-job training.
C) only through job experience.
D) through schooling, job training, and experience.
E) only at birth, that is, it's people's inborn talents.
Answer: D
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
24) Advances in technology and growth in human capital ________ because ________.
A) shift the productivity curve downward; labor and capital become less productive
B) shift the productivity curve downward; labor and capital become more productive
C) shift the productivity curve upward; labor and capital become less productive
D) shift the productivity curve upward; labor and capital become more productive
E) do not shift the productivity curve; there is a movement along the productivity curve
Answer: D
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
25) The expansion of human capital and the discovery of new technologies ________ because ________.
A) are subject to diminishing returns; they shift the productivity curve downward
B) are subject to diminishing returns; they shift the productivity curve upward
C) are not subject to diminishing returns; they shift the productivity curve downward
D) are not subject to diminishing returns; they shift the productivity curve upward
E) are not subject to diminishing returns; they result in a movement along the productivity curve
Answer: D
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
26) Labor productivity increases if
i. human capital decreases.
ii. technology advances.
iii. quality of education decreases.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) Both i and ii
E) Both ii and iii
Answer: B
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, technology
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
27) ________ increases with education, training, and job experience.
i. Physical capital
ii. Human capital
iii. Financial capital
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) both ii and iii
E) i, ii, and iii
Answer: B
Topic: Increase in labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
28) U.S. labor productivity slowed during the 1970s because of
i. increasing government taxes and regulations on production.
ii. the necessity to cope with energy price increases.
iii. inflation, which shortened the horizon over which businesses made their borrowing plans.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) Both i and ii
E) i, ii, and iii
Answer: E
Topic: Eye on the U.S. economy, U.S. labor productivity growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
29) Over the last 50 years, U.S. labor productivity grew the fastest during the ________ because of ________.
A) 1900s; the war on terror and return to the basics of education
B) 1990s; advancements in healthcare due to the unlocking of the human genome
C) 1980s; the invention of the computer and the oil embargo
D) 1970s; an increase in government taxes and expanded regulations
E) 1960s; fast paced technological change and large increases in human capital accumulation
Answer: E
Topic: Eye on the U.S. economy, U.S. labor productivity growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
30) The law of diminishing marginal returns states that
A) output increases at a constant rate as more capital is added.
B) output decreases at a constant rate as more capital is added.
C) as both labor and capital are increased, output does not change.
D) as both labor and capital are increased, output increases at a decreasing rate.
E) output increases at a decreasing rate as more capital is added.
Answer: E
Topic: Law of diminishing marginal returns
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
31) According to the law of diminishing returns, an additional unit of
A) capital produces more output than an additional unit of labor.
B) labor decreases output.
C) capital produces the same amount of output as an additional unit of labor.
D) capital produces more output than the previous unit.
E) capital produces less output than the previous unit.
Answer: E
Topic: Law of diminishing marginal returns
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
32) The shape of the productivity curve reflects the
A) effects of capital accumulation.
B) effects of technological progress.
C) change in labor productivity as human capital increases.
D) law of diminishing marginal returns.
E) effects of population growth.
Answer: D
Topic: Law of diminishing marginal returns
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
33) The productivity curve is a relationship between
A) real GDP per hour of labor and capital per hour of labor, with technology held constant.
B) nominal GDP per hour of labor and capital per hour of labor, with technology held constant.
C) real GDP per hour of labor and capital per hour of labor whenever technological growth occurs.
D) real GDP per unit of capital and capital per hour of labor, with technology held constant.
E) capital per hour of labor and technological growth.
Answer: A
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
34) The productivity curve is a relationship between ________ and ________.
A) real GDP; hours of labor
B) real GDP; capital
C) real GDP per hour of labor; capital
D) capital per hour of labor; labor per hour of capital
E) real GDP per hour of labor; capital per hour of labor
Answer: E
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
35) A diagram of a productivity curve has
A) real GDP per hour of labor on the y-axis and capital per hour of labor on the x-axis.
B) real GDP per hour of labor on the y-axis and hours of labor on the x-axis.
C) capital per hour of labor on the y-axis and real GDP per hour of labor on the x-axis.
D) real wages per hour on the y-axis and real GDP per hour of labor on the x-axis.
E) real GDP per hour of labor on the y-axis and real wages per hour on the x-axis.
Answer: A
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
36) The productivity curve
A) has a positive slope.
B) has a negative slope.
C) is vertical.
D) is horizontal.
E) is U-shaped.
Answer: A
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
37) Suppose that an Intel worker rearranges existing machines and labor and increases the quantity of chips Intel can produce. Using the productivity curve graphed, this innovation would be described as
A) a movement upward along the curve.
B) a movement downward along the curve.
C) a shift of the curve upward.
D) a shift of the curve downward.
E) no change to the productivity curve.
Answer: C
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
38) If capital per hour of labor increases, GDP per hour of labor
A) decreases for a given level of technology.
B) increases because the level of technology advances.
C) increases for a given level of technology.
D) decreases because the level of technology decreases.
E) changes only if technology also advances.
Answer: C
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
39) If capital per hour of labor decreases, real GDP per hour of labor
A) decreases because the level of technology decreases.
B) increases because the level of technology increases.
C) increases for a given level of technology.
D) decreases for a given level of technology.
E) changes only if technology also advances.
Answer: D
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
40) If the level of technology rises, GDP per hour of labor
A) increases for any level of capital per hour of labor.
B) increases because the level of capital per hour of labor increases.
C) decreases for a given level of capital per hour of labor.
D) decreases because the level of capital per hour of labor decreases.
E) does not change because GDP increases only when capital or labor increases.
Answer: A
Topic: Productivity curve, technological advance
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
41) A technological change ________ and a change in the capital stock ________.
A) shifts the productivity curve; shifts the productivity curve
B) shifts the productivity curve; creates a movement along the productivity curve
C) creates a movement along the productivity curve; shifts the productivity curve
D) does not change the productivity curve; creates a movement along the productivity curve
E) does not change the productivity curve; shifts the productivity curve
Answer: B
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
42) The expansion of human capital and the discovery of new technologies ________ because ________.
A) decrease real GDP; they shift the productivity curve downward
B) decrease real GDP; they shift the productivity curve upward
C) increase real GDP; they shift the productivity curve downward
D) increase real GDP; they shift the productivity curve upward
E) increase real GDP; they result in a movement upward along the productivity curve
Answer: D
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
43) Increases in capital per worker ________ because ________.
A) increase real GDP; they shift the productivity curve downward
B) increase real GDP; they shift the productivity curve upward
C) increase real GDP; they create a movement downward along the productivity curve
D) increase real GDP; they create a movement upward along the productivity curve
E) may increase or decrease real GDP; the result is a movement along the productivity curve but the direction depends on other factors not given
Answer: D
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: New
AACSB: Reflective thinking
44) Labor productivity equals ________.
A) real GDP × aggregate hours
B) real GDP ÷ aggregate hours
C) aggregate hours ÷ real GDP
D) aggregate hours × labor productivity
E) aggregate hours ÷ labor productivity
Answer: B
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
45) Labor productivity equals
A) real GDP divided by the capital stock.
B) real GDP divided by the population.
C) total wages divided by real GDP.
D) real GDP divided by aggregate hours.
E) aggregate hours divided by employment.
Answer: D
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
46) If real GDP is $1,200 billion, the population is 60 million, and aggregate hours are 80 billion, labor productivity is
A) $5.00 an hour.
B) $6.67 an hour.
C) $15.00 an hour.
D) $20,000.
E) $150 an hour.
Answer: C
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
47) If aggregate hours are 100 billion hours and labor productivity is $40 an hour, than real GDP equals
A) $100 billion.
B) $40 billion.
C) $100 trillion.
D) $2.5 trillion.
E) $4 trillion.
Answer: E
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
48) Which of the following lists gives factors that increase labor productivity?
A) saving and investment in physical capital, and wage increases
B) expansion of human capital, labor force increases, and discovery of new technologies
C) expansion of human capital, population growth, and discovery of new technologies
D) saving and investment in physical capital, expansion of human capital, and discovery of new technologies
E) labor force increases and wage increases
Answer: D
Topic: Increase in labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
49) Growth in physical capital depends most directly upon the
A) amount of saving and investment.
B) number of firms in the nation.
C) speed of population growth.
D) amount of government expenditures.
E) level of human capital.
Answer: A
Topic: Sources of economic growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
50) The productivity curve shifts upward when
A) physical capital increases.
B) human capital decreases.
C) hours of labor increase.
D) hours of labor decrease.
E) technology advances.
Answer: E
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
9.3 Economic Growth Theories: Old and New
1) Thomas Malthus was an economist who contributed to the ________ theory of growth.
A) classical
B) neoclassical
C) new growth
D) socialist
E) Keynesian
Answer: A
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
2) The Malthusian theory
A) is also called the classical growth theory and predicts that we will run out of resources.
B) is also called the neoclassical growth theory.
C) predicts that the real GDP per person will continue to increase as long as technology increases.
D) claims that the subsistence wage will increase over time.
E) shows that the production function will shift upward continuously.
Answer: A
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
3) A key element of the classical growth theory is that
A) economic growth can be sustained as long as government intervention does not occur.
B) increases in technology drive economic growth.
C) an increase in population leads to increase in labor supply and a decline in real GDP per person.
D) low taxes promote economic growth.
E) market forces drive economic growth.
Answer: C
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
4) The classical theory was developed in the late 18th and early 19th centuries
A) and therefore is not accepted today.
B) during a time of population decline.
C) and has proponents today who fear population growth and overpopulation.
D) and cannot be explained using the modern tool of the productivity function.
E) and still applies to the most developed nations today, though not to the less developed nations.
Answer: C
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
5) Classical growth theory predicts that in the long run there will be
A) zero economic growth.
B) positive economic growth.
C) negative economic growth.
D) sustained increases in the productivity growth rate.
E) sustained increases in economic growth.
Answer: A
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
6) According to classical growth theory, people earn only a subsistence real income because of growth in
A) technology.
B) capital.
C) population.
D) employment.
E) labor productivity.
Answer: C
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
7) Which of the following are predicted by the classical growth theory?
i. Population growth will end economic growth.
ii. Real GDP per person will return to subsistence level.
iii. Technology drives persistent economic growth.
A) i and ii
B) i, ii and iii
C) i only
D) ii only
E) i and iii
Answer: A
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
8) If real GDP per person rises above the subsistence level then, according to classical growth theory,
A) population growth will slow down.
B) a population explosion will occur.
C) labor productivity growth permanently increases.
D) real GDP per person will remain above the subsistence level.
E) real GDP per person will fall below the subsistence level.
Answer: B
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
9) According to classical growth theory, if labor productivity increases,
A) the population grows and eventually real GDP returns to the subsistence level.
B) the population grows but more slowly than real GDP so that people's incomes are permanently higher.
C) the pursuit of profit causes further increases in capital per hour and technology and economic growth continues indefinitely.
D) the growth rate of real GDP per person permanently increases.
E) people save more, which increases the capital per hour even more, and so economic growth continues indefinitely.
Answer: A
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
10) Classical growth theory predicts that increases in real GDP per person will
A) not last because higher income leads to a population explosion.
B) last because higher growth leads to new technology.
C) last because people make choices in the pursuit of higher profits.
D) not last because higher income encourages smaller families and a lower population growth rate.
E) last only if the government directs firms to make more investments in capital and new technology.
Answer: A
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
11) Classical growth theory predicts that economic growth
A) will continue at the classical rate of 3 percent forever.
B) will eventually stop because of population growth.
C) occurs because of hard-working citizens.
D) is merely an illusion.
E) decreases the supply of labor.
Answer: B
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
12) The classical growth theory asserts that
A) economic growth will continue indefinitely.
B) economic growth and population growth complement each other.
C) population growth increases a nation's economic growth.
D) population growth will lead to people earning only a subsistence level of income.
E) population growth leads to more growth in technology.
Answer: D
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
13) In classical growth theory, if real GDP per person is above the subsistence level,
A) the economy will keep growing without limit.
B) population grows and lowers real GDP per person to its subsistence level.
C) technological growth occurs and keeps real GDP per person above its subsistence level.
D) the pursuit of profit will cause economic growth to accelerate.
E) None of the above is correct because the classical growth theory asserts that real GDP per person can never exceed the subsistence level.
Answer: B
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
14) Classical growth theory predicts
A) a slowdown in population growth over time.
B) real GDP per person will remain at the subsistence level over time.
C) sustained increases in economic growth in the long run.
D) the population growth rate slows as real GDP per person rises.
E) sustained increases in the standard of living in the long run.
Answer: B
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
15) The new growth theory was developed by ________ and proposes that ________.
A) Paul Romer; the desire for profits drives increases in real GDP per person
B) Robert Solow; increases in technology growth are responsible for economic growth
C) Thomas Malthus; increases in population drive wages to their subsistence level
D) Adam Smith; markets will determine the appropriate economic growth rate
E) Ben Bernanke; changes in the money supply drive economic growth
Answer: A
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
16) In explaining economic growth, new growth theory stresses the role played by
A) human choices.
B) population moderation.
C) women in the workforce.
D) the participation rate of elderly workers.
E) the government in directing the nation's investments.
Answer: A
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
17) According to the new growth theory, which of the following promote economic growth?
i. discoveries that bring profit
ii. choices that expand human capital
iii. random events that create technology change
A) i and iii
B) i and ii
C) i, ii and iii
D) ii only
E) i only
Answer: B
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
18) In new growth theory, growth in real GDP per person occurs because
i. human capital grows indefinitely.
ii. technology advances as a result of choices individuals make.
iii. profit incentives encourage technological change.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) both i and iii
E) i, ii, and iii
Answer: E
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
19) New growth theory asserts that
i. human capital grows because of choices.
ii. discoveries result from choices.
iii. competition brings profits.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) both i and iii
E) both i and ii
Answer: E
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
20) According to the new growth theory, real GDP per person grows because
A) the population increases.
B) the labor force participation rate increases.
C) people make choices in pursuit of profits.
D) the retirement age increases.
E) the government subsidizes firms' research and development.
Answer: C
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
21) The new growth theory asserts that profits are
A) permanent, because they are derived from discoveries.
B) temporary, because the discoveries that lead to profits are eventually used by all.
C) an illusion, since costs are never fully covered.
D) permanent, because physical activities can be replicated.
E) not an essential component determining whether the economy grows or not.
Answer: B
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
22) The new growth theory asserts that
A) the population growth rate will increase when real GDP per person increases.
B) a discovery can be used by only one person, the discoverer.
C) technology improves slowly while population grows rapidly.
D) production processes can be replicated at many different firms in the economy.
E) eventually people earn only a subsistence living.
Answer: D
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
23) A central theme of the new growth theory is that
A) firms don't really experience profit.
B) humans can work harder than previously thought.
C) the economy doesn't experience diminishing returns.
D) firms don't experience diminishing returns.
E) the government is more efficient than private markets.
Answer: C
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
24) The new growth theory
A) corrects for poor estimates of population growth.
B) eliminates technological advances from the growth picture.
C) applies to only very poor, less-developed nations.
D) explains the source of technological advances.
E) asserts that economic growth can be rapid but can only persist for a limited period of time.
Answer: D
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
25) New growth theory asserts that ________ will lead us to greater productivity and economic growth.
A) new machinery
B) government regulation
C) unlimited wants
D) leisure time
E) nothing
Answer: C
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
26) Which of the following statements is likely to be made by someone who believes in the new growth theory?
A) Population growth will limit long-run gains in real GDP per person.
B) Competition will encourage discoveries of new ideas leading to greater economic growth.
C) Although technological changes increase real GDP, these changes are random and unexplainable.
D) Choices made by human capital are likely to be inefficient.
E) Economic growth will eventually slow.
Answer: B
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
27) The new growth theory's comparison of the economy to a perpetual motion machine implies that
A) permanent growth is not possible.
B) the economy will forever create and destroy jobs.
C) overpopulation will eventually overtake the resources of the planet.
D) technology changes just happen.
E) labor productivity has no influence on the economy.
Answer: B
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
28) Which of the following theories predicts that there can be no sustained rise in real GDP per person above the subsistence level?
i. Classical growth theory
ii. New growth theory
A) i only
B) ii only
C) Neither i nor ii
D) Both i and ii
E) None of the above because whether the rise in real GDP per person is sustained or not depends on what created the rise.
Answer: A
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
29) Classical growth theory predicts that increases in
A) real GDP per person are permanent and sustainable.
B) real GDP per person are temporary and not sustainable.
C) resources permanently increase labor productivity.
D) resources permanently increase real GDP per person.
E) competition increase economic growth.
Answer: B
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
30) If real GDP per person is above the subsistence level then, according to classical growth theory,
A) the population will increase.
B) the population will decrease.
C) the standard of living will continue to improve.
D) labor productivity will increase.
E) more technological advances occur.
Answer: A
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
31) According to classical growth theory, when real GDP per person ________, the population grows.
A) is less than the subsistence real income
B) exceeds the subsistence real income
C) exceeds capital per hour of labor
D) is less than capital per hour of labor
E) is constant
Answer: B
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
32) New growth theory predicts that
A) economic growth is only temporary.
B) economic growth can last indefinitely.
C) economic growth is eroded by changes in taxes.
D) government policies can do nothing to foster increased growth.
E) ultimately people earn a subsistence wage.
Answer: B
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
33) The new growth theory states that
A) technological advances are the result of random chance.
B) technological advances are the result of discoveries and choices.
C) technological advances are the responsibility of the government.
D) the subsistence level income leads to technological advances.
E) it is impossible to replicate production activities.
Answer: B
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
34) According to new growth theory, growth
A) occurs when real GDP greater than the subsistence level.
B) is unending.
C) ends when competition disappears.
D) depends on the population growth rate.
E) cannot be sustained without government help.
Answer: B
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
35) The theory that suggests that our unlimited wants will lead to perpetual economic growth is the
A) classical growth theory.
B) sustained growth theory.
C) old growth theory.
D) new growth theory.
E) Malthusian growth theory.
Answer: D
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
36) According to the new growth theory, ________ is the factor that motivates technological change.
A) random chance
B) profit
C) diminishing returns
D) the replication of activities
E) decisions about how much human capital to acquire
Answer: B
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
9.4 Achieving Faster Growth
1) At its most basic level, economic growth depends on
A) creating the right incentives.
B) saving by the government.
C) government leadership.
D) government's fixing prices to encourage stability.
E) political freedom.
Answer: A
Topic: Preconditions for growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
2) If a country lacks ________, economic growth ________.
A) a democratic form of government; cannot occur
B) a proper incentive system; cannot occur
C) pure capitalism; will be slower compared to other countries
D) a proper incentive system; will occur at a pace suggested by the new growth theory
E) economic freedom; will increase at a faster pace
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
3) The presence of an incentive system that encourages growth
A) guarantees that growth will occur.
B) creates the right conditions for growth to occur.
C) cannot exist in poor countries.
D) existed even in hunter-gatherer societies.
E) means that the government must be a democracy.
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
4) All of the following are preconditions for economic growth EXCEPT
i. property rights.
ii. democracy.
iii. free markets.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) Both i and ii
E) i, ii, and iii
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
5) A key reason why some nations show little or no growth is
A) overpopulation that overuses limited resources.
B) lack of incentives to undertake actions toward growth.
C) too much private property not directed by the government.
D) patents in rich nations that keep technology only for the rich.
E) too much international trade so that all economic growth spills over to foreigners.
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
6) An important condition required for economic growth is
A) a democratic government.
B) a totalitarian government.
C) a libertarian government.
D) economic freedom.
E) the incentive to limit international trade so that all economic growth remains within the country.
Answer: D
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
7) A basic precondition necessary to achieve economic growth is
A) well-functioning factories.
B) well-being of society.
C) a well-functioning legal system.
D) a well-organized work force.
E) a strong central government that directs the nation's research and development activities.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
8) Economic freedom
A) is not important for nations to grow.
B) must come from a democratic government.
C) is founded, in part, on the rule of law.
D) is created when the nation imposes many regulations on businesses.
E) is harmed by having too many property rights.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
9) Economic freedom requires
A) that there are no regulations and restrictions set on businesses and households by the government.
B) the rule of law and the ability to enforce the laws.
C) strong labor unions.
D) freedom to bribe government officials.
E) that the government be a democracy.
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
10) Economic freedom provides the
A) political system that encourages democracy.
B) social system that supports families.
C) production system that discourages property rights.
D) incentive system that encourages growth-producing activities.
E) necessary alternative to free markets.
Answer: D
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
11) Countries that enjoy economic growth
A) have property rights and markets which provide incentives for discovering new technologies.
B) have economies that allow the government to make decisions in everyone's best interests.
C) restrict international trade so that domestic industries can grow.
D) place high taxes on saving and investment.
E) place controls on property rights so that firms are protected from competition.
Answer: A
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
12) For economic freedom to exist,
A) copyright laws must be abolished and markets supervised by the government.
B) democracy must exist.
C) property rights must be protected and markets must be free.
D) human capital must be given away free.
E) money must be free.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
13) Hong Kong is an example of an economy that
A) does not experience economic growth because it is not a democracy.
B) experiences economic growth in spite of the fact that is lacks democratic freedom.
C) grows more slowly than other Asian countries because property rights are not valued.
D) needs to promote investment so that economic growth can occur.
E) lacks economic freedom and therefore experiences the slowest economic growth of all developed economies.
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
14) A condition necessary for a country to achieve economic growth is
A) high tax rates so the government can purchase a lot of capital equipment.
B) strict environmental regulations.
C) economic freedom.
D) government control of the banking system.
E) democracy.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions to economic growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
15) Economic freedom is a precondition for economic growth. Which of the following is a characteristic of economic freedom?
i. A democratic form of government
ii. Property rights must be protected.
iii. The government must support and pay for inventions and innovations.
A) i only
B) ii only
C) Both i and ii
D) Both ii and iii
E) Both i and iii
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
16) Economic freedom is present, at least in part, when
A) there are no property rights to limit people's freedom.
B) there is no private property.
C) people are able to make personal choices.
D) there is no government.
E) money is free.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
17) Economic growth is slow or absent in some economies because those lack
A) political freedom.
B) economic freedom.
C) democracy.
D) cultural freedom.
E) a strong government.
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
18) A key reason why some countries are growing very slowly is
A) they lack a democratic government.
B) they lack economic freedom.
C) their inflation rate is too high.
D) they are too poor, so there is no saving.
E) there is too much competition within their economies.
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
19) A reason why many of the third world countries are not achieving an increase in their standard of living is that they
A) don't have enough natural resources.
B) don't have strong military power to force people to work harder.
C) don't have social institutions with a strong rule of law and economic freedom.
D) strongly encouraged international trade.
E) don't have a strong central government.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
20) Property rights
A) don't include intellectual property.
B) don't include financial property.
C) don't include physical property.
D) include physical, financial, and intellectual property.
E) slow the economic growth by placing limits on who can use what.
Answer: D
Topic: Preconditions for growth, property rights
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
21) Property rights assure people that
A) the government will not confiscate their income or savings.
B) the government will provide a minimum standard of living.
C) the factors of production and goods are owned jointly by the government and the people.
D) economic growth will enhance government involvement in the economy.
E) international trade will be limited.
Answer: A
Topic: Preconditions to economic growth, property rights
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
22) Jose and Julia were discussing the necessary components to achieve economic growth. Jose stated that the economy must include free markets, specialization and trade, and an ethical judicial system. Julia reminded Jose that another key component is
A) freedom of speech.
B) freedom of religion.
C) a guaranteed high rate of return on savings.
D) property rights.
E) democracy.
Answer: D
Topic: Preconditions for growth, property rights
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
23) One possible way of achieving faster economic growth is to
A) regulate the amount of international trade and limit it so that not too much occurs.
B) limit research and development because research and development does not contribute anything to today's production.
C) assign the government ownership of all capital.
D) protect property rights and free markets.
E) tax saving so that people spend more and firms' profits are higher.
Answer: D
Topic: Preconditions for growth, property rights
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
24) Which of the following are important for countries to promote with property rights and incentives if economic growth is to occur?
i. specialization
ii. saving and investment
iii. increases in human capital
iv. discovery of new technology
A) i, ii, iii and iv.
B) ii and iii.
C) iii and iv.
D) ii and iv.
E) i, ii and iv only.
Answer: A
Topic: Preconditions for growth, property rights
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
25) One way to achieve faster growth in GDP per person is to increase the
A) number of women working in the home rather than in the workforce.
B) growth rate of the quantity of money.
C) growth rate of human capital.
D) growth rate of the population.
E) limits on international trade in order to keep more of total spending on domestically produced goods.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions for growth, human capital
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
26) The following government policies will help achieve faster economic growth EXCEPT
A) discouraging saving and encouraging spending.
B) encouraging research and development.
C) establishing and protecting property rights.
D) improving the quality of education.
E) increasing saving.
Answer: A
Topic: Policies for faster growth, saving
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
27) If Turkey wants to promote faster economic growth, it will need to
A) promote incentive systems to encourage saving, research and development, increased trade and improved education.
B) restrict economic freedom so the government has better control of markets.
C) restrict international trade to protects its own workers.
D) promote government intervention to help markets determine incentives.
E) restrict property rights so that individuals can better share inventions.
Answer: A
Topic: Policies for faster growth
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
28) Retirement savings accounts, such as IRAs, help increase economic growth because
A) people have an incentive to work harder and longer hours to save for the future.
B) they keep the interest rates high.
C) savings finances investment.
D) government invests them.
E) they encourage international trade.
Answer: C
Topic: Policies for faster growth, saving
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
29) One possible way of achieving faster economic growth is to
A) encourage saving.
B) protect the economy from international trade.
C) limit investment because investment adds nothing to production today.
D) eliminate property rights because they prevent people from using other people's ideas.
E) tax saving so that people spend more and businesses make more profit.
Answer: A
Topic: Policies for faster growth, saving
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
30) East Asian economies have grown
A) rapidly because of high saving rates.
B) rapidly despite a lack of property rights.
C) slowly because of a lack of property rights.
D) slowly because of low saving rates.
E) rapidly because they virtually eliminated international trade.
Answer: A
Topic: Policies for faster growth, saving
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
31) One of the possible roles governments can play in sponsoring growth is to
A) provide tax incentives to encourage saving.
B) own more of the nation's resources in order to put them to use.
C) close the nation to trade in order to protect its domestic producers.
D) make decisions for its citizens as to the most suitable job.
E) limit the use of property rights in order to decrease the harm they create.
Answer: A
Topic: Policies for faster growth, saving
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
32) Many economists argue that an incentive to save is
A) high income tax rates.
B) a tax on consumption rather than on income.
C) a tax on income rather than a tax on consumption.
D) greater government regulation of the banking and securities industries.
E) strengthening the property rights that savers have to the physical capital they purchase.
Answer: B
Topic: Policies for faster growth, saving
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
33) One possible way of achieving faster economic growth is to
A) abolish the system of patents and copyrights so that everyone can use people's ideas.
B) limit international trade to only a few countries so that the nation is not hurt by too much trade.
C) encourage research and development.
D) limit schooling in order to have more people in the labor force, producing goods and services.
E) promote tax saving so that people spend more and businesses' profits are larger.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions for growth, R&D
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
34) One possible way of achieving faster economic growth is to
A) limit international trade.
B) encourage international trade.
C) limit research and development and concentrate on production of goods and services.
D) abolish the system of patents and copyrights so that everyone can use people's ideas.
E) let the government decide what research and development should be undertaken.
Answer: B
Topic: Policies for faster growth, international trade
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
35) Encouraging international trade will
A) slow economic growth when a country is forced to specialize and trade with other countries.
B) slow economic growth as many workers lose their jobs to foreign workers.
C) speed economic growth as workers diversify their knowledge and limit trade.
D) speed economic growth as workers specialize and trade with others.
E) speed economic growth because international trade limits the harm done by property rights.
Answer: D
Topic: Policies for faster growth, international trade
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
36) The fastest growing nations today
A) are not saving but instead are investing.
B) have erected many trade barriers to protect domestic firms.
C) have the fastest growing exports and imports.
D) have non-democratic political systems.
E) have the government directing all their research and development.
Answer: C
Topic: Policies for faster growth, international trade
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
37) China's growth rate has ________ that of most other countries, ________.
A) topped; but its real GDP per person is still lower than other industrialized countries
B) lagged behind; and its real GDP is close to other Asian economies
C) lagged behind; but its real GDP per person is higher than other Asian economies
D) topped: but its real GDP per person declined in 2008-09
E) equalled; and its real GDP per person declined in 2008-09
Answer: A
Topic: Eye on convergence and gaps
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
38) Governments should promote education because education contributes to the nation's
A) employment.
B) free markets.
C) economic growth potential.
D) international trade.
E) protection of property rights.
Answer: C
Topic: Policies for faster growth, education
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
39) Brian is running for state senator and if elected, pledges to improve economic growth. His plan for economic growth includes increasing spending on public education and providing tax incentives to encourage improved private education. His plan is likely to
A) slow economic growth because it includes a provision for private education.
B) have no effect on economic growth because property rights are not changed.
C) speed economic growth as the quality of resources improve.
D) fail because the provision for private education limits government involvement in education.
E) have no effect on economic growth because government spending cannot affect the economic growth rate.
Answer: C
Topic: Policies for faster growth, education
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
40) If Kenya institutes policies that support economic freedom and growth, it is likely that Kenya will
A) immediately reap the benefits of double digit increase in economic growth.
B) immediately reap the benefits of a 4 percent to 6 percent increase in economic growth.
C) slowly reap the benefits of economic growth as the economy grows over time.
D) lose control of the economy and plunge into a long recession.
E) suffer from too much competition within its economy.
Answer: C
Topic: Faster growth, the difference policy makes
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
41) Which of the following is NOT a necessary precondition for economic growth?
A) economic freedom
B) democracy
C) property rights
D) free markets
E) ALL of the above are necessary preconditions.
Answer: B
Topic: Preconditions for growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
42) Which of the following characteristics is a precondition for economic growth?
i. economic freedom
ii. free markets
iii. active government policy to discourage saving
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) Both i and ii
E) Both ii and iii
Answer: D
Topic: Preconditions for growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
43) Economic freedom means that
A) firms are regulated by the government.
B) some goods and services are free.
C) people are able to make personal choices and their property is protected.
D) the rule of law does not apply.
E) the nation's government is a democracy.
Answer: C
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
44) Property rights protect
A) only the rights to physical property.
B) only the rights to financial property.
C) all rights except rights to intellectual property.
D) rights to physical property, financial property, and intellectual property.
E) the government's right to impose taxes.
Answer: D
Topic: Preconditions for growth, property rights
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
45) Activities that encourage faster growth are
A) high levels of saving and investment in human capital.
B) high levels of consumption and low levels of savings.
C) taxes on saving that serve to encourage more spending and less saving.
D) imposing trade barriers to limit international trade and thereby protect national industries.
E) limiting property rights so that everyone can use any invention.
Answer: A
Topic: Policies for faster growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
46) Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Saving helps create economic growth.
B) Improvements in quality of education are important for economic growth.
C) Free international trade helps create economic growth.
D) Faster population growth is the key to growth in real GDP per person.
E) Economic freedom requires property rights.
Answer: D
Topic: Policies for faster growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
47) In order to increase economic growth, a government can
A) discourage research and development.
B) decrease funding on education.
C) discourage specialization and trade.
D) establish property rights and a legal system.
E) tax saving in order to encourage more spending.
Answer: D
Topic: Policies for faster growth
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
48) Saving
A) slows growth because it decreases consumption.
B) finances investment which brings capital accumulation.
C) has no impact on economic growth.
D) is very low in most East Asian nations.
E) is important for a country to gain the benefits of international trade.
Answer: B
Topic: Policies for faster growth, saving
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
49) A government policy that taxes saving in order to discourage saving and encourage spending will
A) slow economic growth.
B) speed economic growth.
C) create a greater incentive for people to specialize.
D) strengthen people's property rights.
E) increase the growth rate of capital.
Answer: A
Topic: Policies for faster growth, saving
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
50) The fastest growing nations today are those with
A) barriers that significantly limit international trade.
B) the fastest growing exports and imports.
C) government intervention in markets to ensure high prices.
D) few funds spent on research and development.
E) the least saving.
Answer: B
Topic: Policies for faster growth, international trade
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
51) Economic growth is enhanced by
A) free international trade.
B) limiting international trade so that the domestic economy can prosper.
C) discouraging saving, because increased saving means less spending.
D) ignoring incentive systems.
E) increasing welfare payments to the poor so they can afford to buy goods.
Answer: A
Topic: Policies for faster growth, international trade
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
9.5 Integrative Questions
1) Economic growth in Cuba has been slow. What can best explain the slow growth?
A) lack of economic resources
B) lack of incentive mechanisms and economic freedom
C) labor productivity is low.
D) a non-democratic form of government
E) too much competition within the economy
Answer: B
Topic: Integrative
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Integrative
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
2) The idea of continuous economic growth as a "perpetual motion machine" best reflects the prediction of which growth theory?
A) the classical growth theory
B) the traditional growth theory
C) the Keynesian growth theory
D) the new growth theory
E) no growth theory
Answer: D
Topic: Integrative
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Integrative
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
3) Workers in the United States are ________ workers in China because ________.
A) more productive than; workers in the United States have more capital per worker.
B) more productive than; there are more college-educated workers in the United States.
C) less productive than; there are fewer workers in the United States.
D) less productive than; the labor force participation rate is lower in the United States.
E) equally as productive as; China's real GDP per person equals the U.S. real GDP per person.
Answer: A
Topic: Integrative
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Integrative
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
4) The presence of government corruption in some countries
A) slows their economic growth.
B) speeds their economic growth.
C) invalidates the new growth theory's predictions.
D) supports the classical growth theory's predictions.
E) invalidates the neoclassical growth theory's predictions.
Answer: A
Topic: Integrative
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Integrative
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
5) Which of the following policies encourages economic growth?
A) increased taxes on income and business profits
B) reduction of government support of higher education
C) high tariffs and strict import quotas on foreign-made products
D) creation of tax free savings accounts
E) limiting the years people spend in education so that they can start productive work
Answer: D
Topic: Integrative
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Integrative
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
9.6 Essay: The Basics of Economic Growth
1) Why is growth in GDP different from growth in a nation's standard of living? Is it possible for a nation's GDP to grow while its standard of living falls?
Answer: The standard of living is measured by real GDP per person, so growth in the standard of living equals growth in real GDP per person. The growth rate of real GDP per person equals the growth rate of real GDP minus the growth rate of the population. Hence it is indeed possible for a nation's GDP to grow, while its standard of living decreases. This outcome occurs whenever the population grows more rapidly than real GDP.
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
2) How do we calculate growth in a nation's standard of living?
Answer: The standard of living is measured by real GDP per person. Thus growth in the standard of living is calculated using the growth rate of real GDP per person.
Topic: Standard of living
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
3) What is the Rule of 70?
Answer: The Rule of 70 is that the number of years it takes for the level of any variable to double is approximately 70 divided the annual percentage growth rate of the variable.
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Reflective thinking
4) A nation's population was 250 million last year and is 255 million this year. If its real GDP was $8.5 trillion last year and is $8.8 trillion this year, what is its growth rate of real GDP per person?
Answer: Last year real GDP per person equaled ($8.5 trillion)/(250 million) = $34,000 per person. This year, real GDP per person is $34,510 per person. Thus the growth in real GDP per person equals × 100 = 1.5 percent.
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
5) U.S. real GDP per person grew rapidly in the early 1960s. The table above has U.S. real GDP and population for 1961 and 1962.
a. What was U.S. real GDP per person in 1961?
b. What was U.S. real GDP per person in 1962?
c. Between 1961 and 1962, how rapidly did U.S. real GDP per person grow?
Answer:
a. U.S. real GDP per person in 1961 = ($2,432 billion)/(184 million) = $13,217.
b. U.S. real GDP per person in 1962 = ($2,578 billion)/(186 million) = $13,860.
c. The growth rate of real GDP per person equals × 100 = 4.9 percent.
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
6) If a nation's population grows at 2 percent and its real GDP grows at 4 percent, what is the growth rate of real GDP per person?
Answer: The growth rate of real GDP per person equals the growth rate of real GDP minus the population growth rate. Hence, in the question at hand, the real GDP per person growth rate equals 4 percent minus 2 percent, or 2 percent.
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
7) Suppose that real GDP grows at 3 percent per year. What is the growth rate of real GDP per person if the population grows at:
a. 2 percent? What happens to the standard of living?
b. 3 percent? What happens to the standard of living?
c. 4 percent? What happens to the standard of living?
Answer:
a. The growth rate of real GDP per person equals the growth rate of real GDP minus the population growth rate. Hence the growth rate of real GDP per person equals 3 percent minus 2 percent or 1 percent. The standard of living increases because real GDP per person increases.
b. The growth rate of real GDP per person equals 3 percent minus 3 percent or 0 percent. The standard of living does not change because real GDP per person does not change.
c. The growth rate of real GDP per person equals 3 percent minus 4 percent or -1 percent. The standard of living decreases because real GDP per person decreases.
Topic: Growth rate, real GDP per person
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
8) During 2005, real GDP in Ireland grew 9.8 percent. If Ireland maintains this level of growth in the future, real GDP will double in approximately how many years?
Answer: With an annual growth rate of 9.8 percent, the Rule of 70 shows that Ireland's real GDP will double in approximately 70 ÷ 9.8 = 7.1 years.
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
9) Suppose real GDP grows at 7 percent per year and the population grows at 2 percent per year. How many years will it take for real GDP and real GDP per person to double?
Answer: Use the Rule of 70 for both answers. The growth rate of real GDP is given in the question, and so the Rule of 70 directly indicates that real GDP doubles in 70 ÷ 7 = 10 years. To determine the number of years it takes for real GDP per person to double, it is necessary to calculate the growth rate of real GDP per person. The growth rate of real GDP per person equals 7 percent minus 2 percent or 5 percent per year. Hence the Rule of 70 shows that real GDP per person doubles in 70 ÷ 5 = 14 years.
Topic: Rule of 70
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.1
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
9.7 Essay: Labor Productivity Growth
1) Real GDP can increase either because the quantity of labor increases or because labor productivity increases. What is the effect on the standard of living if real GDP increases because
a. the quantity of labor increases?
b. labor productivity increases?
Answer:
a. An increase in real GDP because the quantity of labor increases has no effect on the standard of living.
b. An increase in real GDP because labor productivity increases boosts the nation's standard of living.
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 5: Critical thinking
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
2) What is the effect on real GDP per person if labor productivity increases? What is the effect on the nation's standard of living?
Answer: Real GDP equals (aggregate hours) × (labor productivity). Hence an increase in labor productivity increases real GDP. Real GDP per person equals (real GDP) ÷ (population). Therefore an increase in real GDP with no change in the population increases real GDP per person. The nation's standard of living is measured by real GDP per person. So, an increase in labor productivity boosts real GDP per person and therefore boosts the nation's standard of living.
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 5: Critical thinking
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
3) Real GDP equals $12 trillion and aggregate hours equals 300 billion hours. What does labor productivity equal?
Answer: Labor productivity is defined as (real GDP ÷ aggregate hours), so labor productivity equals ($12 trillion ÷ 300 billion hours) = $40 per hour.
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
4) Labor productivity is $30 per hour and aggregate hours are 165 billion hours. What does real GDP equal?
Answer: Real GDP equals (labor productivity × aggregate hours) = ($30 per hour × 165 billion hours) = $4,950 billion.
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
5) Labor productivity is $20 per hour and aggregate hours are 400 billion hours.
a. What does real GDP equal?
b. Because of technological advances, labor productivity doubles to $40 per hour. Furthermore, assume that aggregate hours decrease to 300 billion hours. What does real GDP equal?
Answer:
a. Real GDP equals (labor productivity × aggregate hours) = ($20 per hour × 400 billion hours) = $8 trillion.
b. Real GDP now equals $12 trillion.
Topic: Labor productivity
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
6) Define labor productivity. Discuss the relationship between labor productivity, human capital growth, and technology change.
Answer: Labor productivity is real GDP per hour of labor, so it equals (real GDP) ÷ (aggregate hours). The expansion of human capital and the discovery of new technology are two factors that increase labor productivity. Increasing human capital increases labor productivity because workers' skills and knowledge increase, which allows them to produce more goods and services without boosting aggregate hours. Similarly, the discovery and use of new technologies allows workers to produce more goods and services without increasing aggregate hours.
Topic: Increase in labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
7) List and explain the three factors that can increase labor productivity.
Answer: The three factors that can increase labor productivity are saving and investment in physical capital, expansion of human capital, and discovery of new technology. Saving and investing in physical capital increases the amount of capital per worker and thereby increases workers' productivity. Increasing the amount of human capital means that workers' skills, knowledge, and talents increase, which thereby increases their productivity. And, the discovery and use of new technologies allows workers to produce more goods and services than before, which increases their productivity.
Topic: Increase in labor productivity
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
8) What are the sources of human capital?
Answer: Human capital, the accumulated skills and knowledge people possess, comes from both formal education and training, and from on-the-job experience. On-the-job experience creates "learning by doing," in which workers become more knowledgeable about the best way to accomplish a task as they do the task.
Topic: Labor productivity, human capital
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
9) Explain the productivity curve and how the components interact.
Answer: The productivity curve is a relationship that shows how real GDP per hour of labor varies as the amount of capital per hour of labor changes with no change in technology. An increase in the amount of capital per hour of labor leads to a movement along a productivity curve. An increase in technology shifts the productivity curve upward.
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
10) What does a productivity curve reflect? What leads to movements along a productivity curve and what leads to shifts in a productivity curve?
Answer: The productivity curve shows the relationship between the amount of capital per hour of labor and real GDP per hour of labor, that is, between capital per hour labor and labor productivity. The curve is upward sloping, but, due to diminishing returns, the slope becomes less steep as capital per hour of labor increases. If the amount of capital per hour of labor changes, there is a movement along the productivity curve. If the amount of human capital increases and/or technology advance occurs, the productivity curve shifts upward.
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 3: Using models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
11) What is the law of diminishing returns? Give an example of what the law of diminishing returns implies.
Answer: The law of diminishing returns is the observation that as the quantity of one input increases with the quantities of all other inputs remaining the same, output increases but by ever smaller increments. Hence, as more workers (or capital) are used by a firm, each additional worker (or unit of capital) increases output, but by less than previous worker (or unit of capital). For instance, a law firm might have one paralegal typing briefs on one personal computer. Hiring an additional paralegal will increase the number of briefs, but with only one personal computer, the additional paralegal will not double the number of briefs. Similarly, buying another computer, while employing only one paralegal, might increase the number of briefs typed, but will not double the number.
Topic: Productivity curve
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.2
Status: Old
AACSB: Analytical thinking
9.8 Essay: Economic Growth Theories: Old and New
1) In the classical theory of growth, what is the final outcome of an increase in growth and labor productivity?
Answer: In the classical growth theory, a rise in labor productivity and the resulting economic growth result in a population explosion that drives real GDP per person back to the subsistence level. In the classical viewpoint, resources are limited and technological change occurs infrequently, so that technological advances are not sufficient to compensate for the lack of resources. Hence, in the long run people earn only a subsistence level of real income.
Topic: Classical growth theory
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
2) Of the two economic growth theories, which is the most optimistic about the chances of real GDP per person growing indefinitely? Which is the most pessimistic? What accounts for the differences?
Answer: The most optimistic is the new growth theory, which concludes that real GDP per person can continue to grow indefinitely. The most pessimistic is the classical theory, which concludes that growth in real GDP per person will stop and that people will produce only the subsistence level of real GDP per person. The difference in the two conclusions can be traced to differences in assumptions in three key areas. First, the new growth theory concludes that technology will advance forever because people, seeking profit, make decisions to develop new technology. Classical growth theory assumes that technological advances are rare and infrequent. Second, the new growth theory assumes that the economy is not subject to diminishing returns. Hence, as the economy accumulates more capital, the returns to capital do not diminish and so the incentive to add yet more capital continues undiminished. The classical growth theory assumes that capital (and labor) is subject to diminishing returns. Thus as more capital is accumulated, the returns diminish, and so the incentive to continue adding more capital disappears. Thus the capital stock eventually stops growing. Finally, the new growth theory assumes that the population does not grow more rapidly as real GDP per person increases. The classical theory assumes that whenever real GDP per person exceeds the subsistence level, rapid population growth occurs and, because of diminishing returns to labor, the increased population drives the level of real GDP back to the subsistence amount.
Topic: New growth theory
Skill: Level 2: Using definitions
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
3) What do the classical growth theory and the new growth theory predict for global growth amongst different nations? Comment on the accuracy of the predictions.
Answer: The classical growth theory predicts that nations will produce only the subsistence level of real GDP per person. This prediction is incorrect. According to the theory, each country is driven to the subsistence level by increased population growth whenever real GDP per person exceeds the subsistence amount. Hence the classical theory predicts that the nations with the highest levels of real GDP per person will be the nations in which real GDP per person is falling the most rapidly. This prediction also is wildly at variance with the facts.
The new growth theory predicts that nations will grow indefinitely and that the growth rate depends on the incentives within each nation to save, invest, accumulate human capital, and develop new technology. Hence the new growth theory predicts that real GDP per person will converge among some nations (those with similar incentives) while the gaps in real GDP per person among other nations will persist. This prediction is accurate.
Topic: Growth in the global economy
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.3
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
9.9 Essay: Achieving Faster Growth
1) What is economic freedom and why is it important for economic growth?
Answer: Economic freedom is a condition when people are able to make their own choices, their private property is protected, and they are free to trade in markets. Economic freedom is a necessary precondition for economic growth because all three aspects of economic freedom are highly growth enhancing. People are the best judges of their own interests and abilities, so allowing them to make their own decisions creates the best decisions about what activities will be undertaken. Protecting private property is necessary in order to give people the incentives to specialize and trade as well as to save and invest, all actions that will increase economic growth. Letting people trade in free markets again respects people's abilities to make the best decisions for themselves, and also increases people's incentives to specialize and trade.
Topic: Economic freedom
Skill: Level 1: Definition
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
2) Why is economic growth so slow or non-existent in many third world countries? What policies would you propose to improve the situation?
Answer: Slow-growing third world countries generally lack the necessary preconditions for economic growth: economic freedom, secure property rights, and freely functioning markets. In many of these nations, a corrupt legal system and government means that the rule of law and property rights are absent. In order to increase economic growth in these nations, policies that create economic freedom, secure property rights, and free markets must be adopted. It does not matter if these policies are adopted by a democratic government or by an authoritarian government, the key point is that they are necessary for the nation to grow. Thus, specific policies include creating an efficient legal system that respects the rule of law and enforces property rights and contracts; eliminating government corruption that undermines the rule of law; and, in order to establish free markets, decreasing government bureaucracy and limits to trade, such as high taxes, regulations, and import bans.
Topic: Preconditions for growth, economic freedom
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
3) What policies can a government undertake to achieve faster economic growth?
Answer: There are several policies a government can undertake. First the government must insure that the preconditions for growth are present. The government must insure that economic freedom exists, that property rights are enforced, and that markets are free. After these crucial preconditions are in place, the government can create incentive mechanisms to save, invest, and innovate; can encourage saving; can encourage research and development; can encourage international trade; and can improve the quality of education.
Topic: Policies for faster growth
Skill: Level 4: Applying models
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
4) A country's leadership believes that the neoclassical growth theory is correct. The country already has the necessary preconditions for growth, so suggest policy changes the government might enact to help speed economic growth.
Answer: The policy changes should encourage technological innovation and capital formation because these are the key engines of growth within the neoclassical growth theory. Hence, the government should encourage research and development, possibly by directly funding research and development. In addition, the government should support policies that increase saving, because an increase in saving will lead to increased investment and hence new capital, some of which will have the new technologies embodied in it.
Topic: Policies for faster growth, research and development
Skill: Level 5: Critical thinking
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
5) Why are the governments of developed countries concerned about the quality of education in their countries? What effect does education play in determining the country's economic growth rate and its standard of living? Why does it have this effect?
Answer: Improving the quality of education is an important policy that the government can undertake to increase the nation's economic growth rate. A higher quality education increases the nation's human capital. Increases in human capital boost labor productivity and, in turn, the increase in labor productivity raises the nation's economic growth rate as well as its standard of living.
Topic: Policies for faster growth, education
Skill: Level 5: Critical thinking
Section: Checkpoint 9.4
Status: Old
AACSB: Written and oral communication
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhdY8wTqcXaF_bnRz1UgHOvcn9MIWkM6eziM1V98T5QRBsBZ0b8r18yKVCpyPKUBDcNTR4IT8Pcv5HgElqfp9wY-MYFi6_B6syjfdGZkQ2zZMKK1Ga4VcGu6HtaWdnEqO75nrMKPT041WU//?imgmax=800)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi965FEDKNtwB9Q3lQcwqclo3R4As0VVX5G0xb3K4Z2IQfBmNoOe61kUidyqAhOMxoklaPZg67Oixv3N7_dbF31nFvwF7jPFslX64S-GcU5xfVs0PBZ9PRYO_H8kgQSukXocLxpi7SQTos//?imgmax=800)
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgoZHMPRzgI8JNSqz4wK_QX3rZHquYWbBOVv6ANrPJHTGG5EfDZE-wyhIKsaAePvrHVNz_enTpuNPEcBmUCVfPMalaKFX5HzixIeC9qm9yoQoKcaBBLX5abUzWmS9Mm3Rd1yNxaj88iB_8//?imgmax=800)
![clip_image008[4] clip_image008[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh6kfWFF7H0_7ad6OnzPlzOrCD33kyHubSGyUig3XOm-yesnp3JG95AS49K0Km27PcHNZmA8E8WClD7hVkKr_CqIsyD9sDLkKIj-ib33fd-8p2TWagWfvzPLe979kRF1htcGXD6JJK4Rv0//?imgmax=800)
![clip_image010[4] clip_image010[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj-uyi1KtvqCUdYL3tqwZAVJUqVLnpQxbF5_EvOveFEI5XR6d-JQNobEmdts4knZyr0yGWMRhYU_jcE1I308939xcaubseS02MWMXbNhW3Cwh09bgqZgO_tXVmI35dgb-BS-llIqx6yV7g//?imgmax=800)
![clip_image014[4] clip_image014[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiRnTAHwreUoMxF2E46y8krh8NmXsnc42QrxuTuwb2pNoV8PBNJgCChoq3O8J5pdIkZnvJYfHD5cBa5Gr0eWozHgkVnJf9FCfmlgVuCl1zYgGsskgz9DpAgNMNaUbkgSOM9icoYXt9EJdU//?imgmax=800)
Investing online has been a main source of income, that's why knowledge plays a very important role in humanity, you don't need to over work yourself for money.All you need is the right information, and you could build your own wealth from the comfort of your home!Binary trading is dependent on timely signals, assets or controlled strategies which when mastered increases chance of winning up to 90%-100% with trading. It’s possible to earn $10,000 to $20,000 trading weekly-monthly, just file a complaint with Mr. William, I had almost given up on everything about binary trading and ever getting my lost funds back, till i met with him, with his help now i have my lost funds back to my bank account and I can now trade successfully with his profitable strategies and software!! Email: GLOBALFXINVESTMENT3@GMAIL.COM
ReplyDeletegolden goose outlet
ReplyDeletebape official
hermes birkin bag
golden goose outlet
goyard
jordan shoes
yeezy
off white outlet
supreme
bape hoodie
Essential Foundations of Economics 7e" underscores the fundamental pillars of economic understanding. How VPN Choose This title promises a comprehensive exploration of core concepts, shaping readers' comprehension of market dynamics, resource allocation, and societal impacts.
ReplyDeleteGreat Blog❤️❤️❤️🇺🇸🇺🇸🇺🇸🇺🇸❤️❤️❤️🇺🇸🇺🇸🇺🇸🇺🇸❤️❤️❤️❤️Investment is one of the best ways to achieve financial freedom. For a beginner there are so many challenges you face. It's hard to know how to get started. Trading on the Cryptocurrency market has really been a life changer for me. I almost gave up on crypto at some point not until saw a recommendation on Elon musk successfully success story and I got a proficient trader/broker Mr Bernie Doran , he gave me all the information required to succeed in trading. I made more profit than I could ever imagine. I'm not here to converse much but to share my testimony; I have made total returns of 2.6BTC from an investment of just 0.6BTC. Thanks to Mr Bernie I'm really grateful,I have been able to make a great returns trading with his signals and strategies .I urge anyone interested in
ReplyDeleteINVESTMENT to take bold step in investing in the Cryptocurrency Market, you can reach him on WhatsApp : +1(424) 285-0682 or his Gmail : BERNIEDORANSIGNALS@GMAIL.COM, bitcoin is taking over the world.
✍🏻✍🏻✍🏻✍🏻✍🏻