CHEM 2: Chemistry in Your World, 2nd Edition solutions manual and test bank John L. Hogg
1. Answer will depend on each person's experience.
2. Change
a. Formation of snowflakes is a physical change because liquid water crystallizes to form solid water; the process can be reversed by melting the snowflake.
b. Rusting of iron is a chemical change. Iron combines with oxygen to form a new substance.
c. Ripening of fruit is a chemical change; the numbers of fragrant esters and sugars change.
d. Fashioning a table from a piece of wood is a physical change; the shape of the piece of wood is mechanically altered.
e. Fermenting grapes is a chemical change; sugars are converted to alcohol and carbon dioxide.
f. Boiling a potato is a chemical change; the molecules in the potato are converted to smaller ones that are more easily digested and that taste differently.
3. No, they would be the same substance.
4. Density, melting point, boiling point, odor, color. For example, water has a density of 1 g/cm3, a melting point of 0°C, a boiling point of 100°C, no odor, and no color.
5. This fact illustrates that one chemical can have many different uses depending on its quantity. Utilization of a small amount of nitroglycerin in treating angina outweighs the risks while when used in larger quantities, the risks can be reversed like when it is used as an explosive.
6. Chemical and Physical properties
a. physical property
b. physical property
c. chemical property
d. physical property
e. chemical property
f. chemical property
7. This answer can vary between students, but the combustion of gasoline to propel vehicles is an example of a useful chemical reaction. This reaction is a chemical change because the liquid gasoline is converted to heat and gases. Another constructive example is the burning of coal to heat water into steam, which is then used to turn a turbine and produce electricity. The combustion of coal results in a flame plus other gases. The above two examples are examples of chemical changes because the products have a different chemical formula than reactants or another way to look at this reaction is that it is not reversible. On the other hand, a destructive reaction is the use of ammonia nitrate to construct bombs for devastation. This compound is a solid but mixed with the correct reactants will produce a flame plus a rapid expansion of gases that makes the explosion. The products formed in this reaction are definitely different than the starting materials.
8. Aggregation
a. element, contains only Hg atoms
b. mixture of water, minerals, proteins, fats
c. compound, contains only one kind of molecule (H2O)
d. mixture of cellulose, water. Wood changes weight when dried.
e. mixture of dye and solvent
f. mixture of water, caffeine, tea extract
g. compound, solid pure water containing only one kind of molecule
h. element, contains only C atoms
i. element, contains only Sb atoms
9. a. tin: solid
b. bromine: liquid
c. dysprosium: solid
d. xenon: gas
e. samarium: solid
f. lithium: solid
g. mercury: liquid
h. iodine: solid
10. a. The role of antifreeze is to prevent freezing, and it ceases to function when it is itself frozen. This change of state is a physical change (liquid to solid).
b. Burning is the process of a material combining chemically with oxygen.
c. The change observed, where a gas is produced from the combination of a liquid and a solid, is an example of a chemical change.
d. Ice is the solid form of water. This is an example of a physical change.
e. Digestion is the process in which food is broken down into nutrients. This requires a chemical change. An example of this would be the conversion of carbohydrates into fat.
11. a. S−I−Ne; sulfur−iodine−neon
b. Cr−Y; chromium−yttrium
c. V−Ir−U−S; vanadium−iridium−uranium−sulfur OR V−I−Ru−S; vanadium−iodine−ruthenium−sulfur
d. Re−Si−S−Ta−N−Ce; rhenium−silicon−sulfur−tantalum−nitrogen−cerium OR Re−S−I−S−Ta−N−Ce; rhenium−sulfur−iodine−sulfur−tantalum−nitrogen−cerium
e. Cr−Os−Sb−O−W;chromium−osmium−antimony−oxygen−tungsten OR Cr−Os−S−B−O−W; chromium–osmium–sulfur–boron–oxygen–tungsten OR Cr−O−S−Sb−O−W; chromium–oxygen–sulfur–antimony–oxygen–tungsten OR Cr−O−S−S−B−O−W; chromium–oxygen–sulfur–sulfur–boron–oxygen –tungsten
f. Fe−Nd−Er; iron–neodymium–erbium
g. Ac−Cu−Se; actinium−copper–selenium OR Ac−C−U−Se; actinium–carbon–uranium–selenium
12. answers depend on each student's name.
13. answers depend on student’s choice of word
14. a. mendelevium, named for Dmitri Mendeleev, who is credited with the development of the periodic table
b. potassium, named for the source from which it was first identified, potash (plant ashes). The elemental symbol of K is derived from the Latin word kalium.
c. californium, a nonnatural element first prepared at the University of California−Berkeley
d. bohrium,named for Neils Bohr, a physicist who contributed to a modern understanding of atomic structure
e. iridium, named because a pure sample of the element is iridescent
f. ytterbium, named for the mineral yttrie from which it was first isolated, near the Swedish village of Ytterbi
g. curium, named for Marie Curie, an early pioneer in understanding radioactivity
15. a. Cu, Co
b. Cu, Cr, Ce
c. W, Ti, Sn
d. Tl, Th
e. N, Ni
f. Carbon, calcium
g. Fe, F
h. N, Ni, Ne
16. Properties of iron do not change because all particles in iron are atoms of iron. Steel is a mixture of iron and other atoms. The type of steel depends on what is added to the iron.
17. False, a molecule is the smallest part of a compound.
18. True
19. False, a molecule is the smallest part of a compound.
20. True
21. A mixture of sand and salt can be separated by adding water to the mixture. The salt will dissolve in the water while the sand will not and settle to the bottom. Filtration of the solution will result in the capture of sand on the filter paper while the dissolved salt will pass through the funnel (filtrate). The sand can be identified because it is not soluble in water and can be recovered by filtering. The salt can be recovered from the filtrate by evaporating the water.
22. Sources of elements
| Element | Major Source | Compound |
| nitrogen | air | ammonia, NH3 |
| sulfur | Underground deposits | sulfuric acid, H2SO4 |
| chlorine | sea water | sodium chloride, NaC1 |
| magnesium | Milk of Magnesia, sea water | magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2 |
| cobalt | Mineral deposits | cyanocobalamin, Vitamin B12 |
23. Atrazine, C8H14N5Cl, contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine.
24.Cytoxan, C7H15O2N2PCl2
a. twenty−nine, 29 atoms total
b. carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, chlorine
c. 15 hydrogens/2 nitrogen
d. yes, it is organic
a. BonAmi kitchen and bath cleanser
b. Coca Cola
c. Gatorade
d. Coca Cola
e. Skippy Peanut Butter
f. Kraft Grated Parmesan Cheese
g. Morton's Iodized Salt
h. Oil of Olay
i. Mylanta
j. Kellogg's Frosted Mini−Wheats
26. Materials and Phases
| SOLID | LIQUID | GAS | |
| Pure substances | iron, Fe; copper, Cu | octane, C8H18 | dry ice, CO2 mercury, Hg; helium, He; nitrogen, N2 , methane, CH4 |
| Mixtures | Butter, Steel, 14 K "gold" | homogenized fuel (hydro− carbons mixed with mercaptans), milk, coffee, sea water | Natural gas, a person's exhaled breath (CO2, O2, H2O) |
27. (c) The identity of the atoms in the reactants has to be the same as the products. The number of atoms on each side of the equation must also be equal.
28. Yes, a mixture of H2 and O2 can exist at room temperature. This mixture will be stable as long as no spark or activation energy is added. A reaction produces water, H2O, which contains both elements.
29. N2 + 3 H2 ® 2 NH3
30. (d) reactant; products
31. Four kinds of energy
a. Electrical energy can be generated by chemical reactions used in alkaline batteries and car batteries.
b. Heat energy can be generated by chemical reactions involving combustion or burning of gasoline.
c. Light energy can be generated by chemical reactions used by fire flies or in glow sticks.
d. Mechanical energy can by generated by using water behind a dam to turn a turbine or the alternator on a car using the belt of the engine.
32. Reactions in words
a. Two sodium atoms react with one chlorine molecule to form two formula units of sodium chloride solid.
b. One nitrogen molecule reacts with three chlorine molecules to produce two molecules of nitrogen trichloride.
c. One molecule of carbon dioxide reacts with one molecule of water to produce one molecule of carbonic acid.
d. (d) Two molecules of hydrogen peroxide react to produce one molecule of oxygen gas and two molecules of water liquid.
33.Balance
a. On the left side of the arrow, "2 Na" means 2 Na atoms; one Cl2 molecule contains 2 Cl atoms. On the right side 2 NaCl units contain 2 Na atoms and 2 Cl atoms.
b. On the left one N2 molecule contains 2 N atoms and 3 Cl2 molecules contain 6 Cl atoms. On the right 2 NCl3 molecules contain a total of 2 N atoms and 6 Cl atoms.
c. On the left there are 1 C atom, 2 H atoms and 2 + 1 = 3 O atoms. On the right there are 1 C atom, 2 H atoms and 3 O atoms.
d. On the left there are 4 H atoms and 4 O atoms in 2 molecules of H2O2. On the right there are 4 H atoms in the 2 molecules of water; there are also 2 O atoms in the 2 water molecules and 2 more O atoms in the O2 molecule for a total of 4 O atoms.
34.For (b) the reactants are nitrogen and chlorine; the product is nitrogen trichloride. For (d) the reactant is hydrogen peroxide; the products are water and oxygen.
35.Testing balances
a. No. The reactant side contains 1 silver atom, 1 nitrogen atom, 1 sulfur atom, 2 sodium atoms and 7 oxygen atoms while the product side contains 2 silver atoms, 1 nitrogen atom, 1 sulfur atom, 1 sodium atom and 7 oxygen atoms.
b. Yes. The reactant side contains 1 silver atom, 1 nitrogen atom, 1 hydrogen atom, 1 chlorine atom and 3 oxygen atoms while the product side contains 1 silver atom, 1 nitrogen atom, 1 hydrogen atom, 1 chlorine atom and 3 oxygen atoms.
36. a. 2 K(s) + 2 H2O(l) ® 2 KOH(s) + H2(g)
b. CO2(g) + H2O(l) ® H2CO3(l)
37. The tea in tea bags is a mixture. It can be partially separated by dissolving some water−soluble substances with hot water. Instant tea is a mixture of the water− soluble substances in tea.
38. Pure substances in the kitchen
a. Baking soda contains only sodium bicarbonate molecules
b. Granulated sugar contains only sucrose molecules
c. Table salt contains only sodium chloride molecules
d. An iron skillet contains only iron atoms
e. Aluminum foil contains only aluminum atoms
f. Water contains only water molecules
39. Unit conversions
a. 1 gram = 1000 milligrams
b. 1 kilometer = 1000 meters
c. 1 gram = 100 centigrams
40. Mass measured in grams. Length is measured in meters. Volume is measured in liters.
41. Units
a. 9 cal/g; no
b. 100 cm/m; no.
c. 1.5 g/mL; yes, grams/milliliter is mass/volume.
d. 454 g/lb.; no.
42. Yes, a 2 quart bowl will hold 1.89 L. One liter is 1.06 quarts. One quart equals 0.94 3 liters.
43. 5.5 acres/55 cows
44. The milligrams can be converted to grams using the factor 1000 mg = 1 g.
200 mg × 1 g = 0.200 grams
1000 mg
The milligrams can be converted to micrograms using the factor 1000 µg = 1 mg.
200 mg × 1000 µg = 200,000 µg
45. 10 km × (1000 m/1 km) = 10,000 m
46. The answer is 3000 mg protein / 1 oz. cereal
47.Unit conversion
a. 0.04 m
b. 43 mg
c. 15500 mm
d. 0.328 L(e) 980 g
48. 163 kg ´ (1000 g / 1 kg) = 163,000 g
49. 70 kg ´ (1000 g / 1 kg) = 70,000,000 mg
50. Aspirin
The milligrams can be converted to grams using the factor 1000 mg = 1 g.
51. (a) 8.0 ´ 107 (b) 3.0 ´ 105 (c) 1.6 ´ 10−5 (d) 9.7 ´ 101
52. The exponent on "10" can be determined by counting the number of places the decimal point must be moved to the left(+) or the right(−) to give a coefficient between 1 and 10. In "a" the decimal point must be moved 6 places to the left so exponent is +6.
a. 8. × 106
b. 7.5 × 10−5
c. 2.36 × 1010
d. 3.7 × 104
e. 6.492 × 103
f. 2.8 × 10−8
53. Units
a. 450,000,000 watts
b. 4,500,000 bulbs
54. The prefix “giga" equals 1,000,000,000 so 60 gigabytes is 60,000,000,000 bytes.
55. 22,420 g
56. Use the definition for density, D = mass/ volume. V = 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm = 1000 cm3.
Mass = D × V = (11.4 g/cm3)(1000 cm3) =11,400 g (or 10,000 rounded to 1 significant digit)
57. The mass of the Al object is 0.34 as much as the mass of the Fe object.
58. 16 fluid ounces
59. 128 fluid ounces
60. 1640 feet
61. 7.73 grains
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Which of the following is not one of the common states of matter?
| a. | solid |
| b. | plasma |
| c. | liquid |
| d. | gas |
ANS: B
2. Which of the following is one of the classes of pure substances?
| a. | compound |
| b. | homogeneous mixture |
| c. | solution |
| d. | heterogeneous mixture |
ANS: A
3. Which is not a mixture?
| a. | pure water |
| b. | mayonnaise |
| c. | strawberry Kool-Aid® drink |
| d. | rock |
ANS: A
4. Most samples of matter occur in nature as
| a. | elements. |
| b. | compounds. |
| c. | homogeneous samples. |
| d. | mixtures. |
ANS: D
5. Separating a mixture of iron and sulfur can be done
| a. | by filtration. |
| b. | dissolving in water. |
| c. | with a magnet. |
| d. | by burning. |
ANS: C
6. Which statement describes a physical property of oxygen?
| a. | Oxygen supports burning of gasoline. |
| b. | Oxygen has a density of 0.0014 g/mL. |
| c. | Oxygen is required for human metabolism of food. |
| d. | Oxygen combines with iron causing the formation of rust. |
ANS: B
7. Which is a chemical property?
| a. | boiling point |
| b. | state |
| c. | odor |
| d. | flammability |
ANS: D
8. A process is probably a chemical reaction if
| a. | it produces light. |
| b. | a solid appears when two solutions are mixed. |
| c. | bubbles start to form when two substances are mixed. |
| d. | all of these |
ANS: D
9. Which of the following is not a chemical change?
| a. | burning charcoal |
| b. | rusting iron |
| c. | melting ice |
| d. | baking bread |
ANS: C
10. Which term describes energy?
| a. | motion |
| b. | heat |
| c. | light |
| d. | all of these |
ANS: D
11. Alfred Nobel ____________?
| a. | discovered dynamite |
| b. | proposed the metric system |
| c. | developed the STM, scanning tunneling microscope |
| d. | discovered kinetic energy |
ANS: A
12. Which mixture is heterogeneous?
| a. | salt and water |
| b. | water and oil |
| c. | sweetened hot tea |
| d. | Ivory soap bar |
ANS: B
13. The element whose name is derived from the Latin aurum, meaning shining dawn
| a. | gold. |
| b. | aluminum. |
| c. | silver. |
| d. | chromium. |
ANS: A
14. Which of the following elements is a metal?
| a. | Ca, calcium |
| b. | Na, sodium |
| c. | Hg, mercury |
| d. | all of these |
ANS: D
15. Sublimation is a characteristic physical property of
| a. | chlorine (Cl2, liquid). |
| b. | oxygen (O2, gas). |
| c. | bromine (Br2, liquid). |
| d. | iodine (I2, solid). |
ANS: D
16. What information is not provided by the formula, C4H10, for butane?
| a. | butane being an organic compound |
| b. | the molecular formula |
| c. | the relative number of atoms of each kind |
| d. | the shape of the molecule |
ANS: D
17. Which of the following sets, is a list of the symbols for an element and a compound (in that order)?
| a. | Mg, CO |
| b. | CO, CO2 |
| c. | CO, Co |
| d. | H2O2, P |
ANS: A
18. Which of the following sets, is a list of the symbols that could represent the following substances, respectively?
lead a compound of equal parts hydrogen and oxygen elemental oxygen
| a. | PB, H2O2, O |
| b. | Pb, HO, O |
| c. | Pb, H2O2, O2 |
| d. | PB, HO, O2 |
ANS: C
19. In the balanced equation, 2 Al + 6 HCl ® 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2, the sum of the coefficients of the reactants is
| a. | 5. |
| b. | 8. |
| c. | 13. |
| d. | none of these |
ANS: B
20. The equation, 2 C(s) + O2(g) ® 2 CO(g), tells us
| a. | the number of atoms of each kind in reactants and products is the same. |
| b. | carbon monoxide (CO) is a product. |
| c. | two atoms of carbon undergo reaction. |
| d. | all of these |
ANS: D
21. How does the known number of nonmetals compare to that of metals?
| a. | There are fewer metals. |
| b. | There are an equal number of each. |
| c. | There are fewer nonmetals. |
| d. | This cannot be predicted because not all metals and nonmetals have been discovered. |
ANS: C
22. What prefix is the largest?
| a. | mega |
| b. | centi |
| c. | micro |
| d. | kilo |
ANS: A
23. A person weighs 165 lbs. Which of the following would calculate their mass in kilograms if 2.2 lbs = 1 kg?
| a. | 165 ´ 2.2 |
| b. | 165 ÷ 2.2 |
| c. | 2.2 ÷ 165 |
| d. | 165 + 2.2 |
ANS: B
24. The quantity 10-9 (one billionth) is designated by the prefix
| a. | pico. |
| b. | nano. |
| c. | centi. |
| d. | mega. |
ANS: B
25. Which of the following would convert 15 L of gasoline to gallons? (1.06 qt = 1 L ; 4 qts = 1 gal)
| a. | (15) (1.06/1) (1/4) |
| b. | (15) (1/1.06) (4/1) |
| c. | (15) (1.06/1) (4/1) |
| d. | (15) (1/1.06) (1/4) |
ANS: A
26. An example of a homogeneous mixture is
| a. | oil in water. |
| b. | a salt water solution. |
| c. | a suspension. |
| d. | a pure substance. |
ANS: B
27. Which of the following is not a pure substance?
| a. | pure gold |
| b. | clean air |
| c. | refined sugar |
| d. | distilled water |
ANS: B
28. Which state of matter is composed of charged particles which are dramatically affected by electric and magnetic fields?
| a. | solids |
| b. | liquids |
| c. | gases |
| d. | plasmas |
ANS: D
29. How many categories of pure substances exist?
| a. | 2 |
| b. | 3 |
| c. | thousands |
| d. | about 100 |
ANS: A
30. A pure substance which can be decomposed into two or more pure substances is a(n)
| a. | element. |
| b. | compound. |
| c. | mixture. |
| d. | colloid. |
ANS: B
31. For which of the following is it necessary that there be a definite composition which cannot vary?
| a. | mixture |
| b. | solution |
| c. | compound |
| d. | colloid |
ANS: C
32. How many phosphorus atoms are in the formula H3PO4?
| a. | 4 |
| b. | 3 |
| c. | 7 |
| d. | 1 |
ANS: D
33. How many chemical formulas are in this chemical equation?
P4(s) + 6 F2(g) ® 4 PF3(g)
| a. | 2 |
| b. | 3 |
| c. | 4 |
| d. | 11 |
ANS: B
34. Which of the following is an SI unit of ?
| a. | pound |
| b. | kilogram |
| c. | quart |
| d. | calorie |
ANS: B
35. Potential energy is defined as
| a. | heat energy. |
| b. | energy associated with motion. |
| c. | stored energy. |
| d. | the ability to do work. |
ANS: C
36. Which of the following is a physical change?
| a. | souring of milk |
| b. | ripening of fruit |
| c. | frying an egg |
| d. | melting |
ANS: D
37. The simplest form of matter is a(n)
| a. | element. |
| b. | mixture. |
| c. | compound. |
| d. | solution. |
ANS: A
38. Which of the following is a compound?
| a. | mercury |
| b. | blood |
| c. | sugar |
| d. | air |
ANS: C
39. How would you separate a mixture of salt, sand, and water?
| a. | by filtration, followed by evaporation |
| b. | freezing, followed by melting |
| c. | separating with tweezers, followed by evaporation |
| d. | by filtration, followed by burning |
ANS: A
40. Which of the following is a physical property?
| a. | freezing point |
| b. | color |
| c. | odor |
| d. | all of the above |
ANS: D
41. Which of the following is an example of a chemical change?
| a. | boiling water |
| b. | iodine sublimating |
| c. | barbecuing a steak |
| d. | breaking a piece of glass |
ANS: C
42. Identify the nonmetal among those listed below.
| a. | Fe |
| b. | Na |
| c. | S |
| d. | Ag |
ANS: C
43. What is the coefficient in front of iron when the following equation is balanced?
Fe + O2 ® Fe2O3
| a. | 1 |
| b. | 2 |
| c. | 4 |
| d. | 6 |
ANS: C
44. How many millimeters are in 100 cm?
| a. | 10 |
| b. | 1000 |
| c. | 100 |
| d. | 1 |
ANS: B
45. Which of the following has the highest kinetic energy?
| a. | boulder on the top of hill |
| b. | water behind a dam |
| c. | a ball falling from a 3 story building |
| d. | a piece of wood |
ANS: C
46. What kind of change is depicted in the following image?
| a. | chemical change |
| b. | physical change |
| c. | both a chemical change and a physical change |
| d. | There is no change shown in the image. |
ANS: A
TRUE/FALSE
1. A pure substance which can be decomposed into two or more pure substances is called a mixture.
ANS: F
2. 10 mg is larger than 100 ng.
ANS: T
3. Glucose has the chemical formula C6H12O6. In one molecule of glucose there are 24 atoms.
ANS: T
4. The density of copper is 8.96 g/mL and that of gold is 19.3 g/mL. The ratio of the mass of a 10 mL block of copper to a 10 mL block of gold is 0.464.
ANS: T
5. The most common unit of volume used in chemistry is the millimeter.
ANS: F
6. In order to convert a measurement for the element mercury from mass to volume, one would multiply the starting measurement by the following factor.
ANS: F
COMPLETION
1. The chemical symbol for copper is_________.
ANS: Cu
2. Mg is the chemical symbol for ____________________.
ANS: magnesium
3. There are ____________mg in exactly 10. g.
ANS:
10,000
10000
104
4. The SI multiple of 10–3 is indicated in a unit with the common prefix _________.
ANS: milli
5. 1 Mm = _______m
ANS:
106
1,000,000
1000000
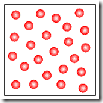
Use the pictures below to answer the following questions.
| a. | c. | ||
| b. | d. |
1. Which figure above depicts a homogeneous mixture?
2. Which figure above depicts a heterogeneous mixture?
3. Which figure above depicts a compound?
4. Which figure above depicts an element?
1. ANS: C
2. ANS: B
3. ANS: D
4. ANS: A
No comments:
Post a Comment