Hunt - Marketing - 1e, solutions manual and test bank 0077861094

Use this Instructor’s Manual to facilitate class discussion and incorporate the unique features of the text’s highlights. Follow-up via the Connect exercises is then encouraged to provide a holistic understanding of the chapter. Click here to access the Connect Instructor’s Manual for helpful suggestions, recommendations and time-saving hints.
chapter FORECAST
This chapter explores the importance of strategic planning in marketing. Executing a thoughtful strategic marketing plan is the most likely path to sustainable business success. The chapter examines the role of a mission statement, situation analysis, marketing strategy, global marketing strategy, and other elements of an effective marketing plan. As you read through the chapter, consider the following key questions:
1. Why is strategic planning important for marketing?
2. What elements should a marketing plan include?
3. How do I evaluate the effectiveness of a firm’s
mission statement?
4. What tools can I use to analyze my firm’s situation externally and internally?
5. What strategic directions can a firm take?
6. How does globalization affect marketing strategy?
7. Why is strategic planning critical for nonprofit
organizations?
Executive perspective
| Michael Friloux Senior Vice President of Business Development, Citynet
Michael Friloux, computer science major turned marketer, attributes his success to social skills, work ethic and personal integrity. He explains how taking responsibility for marketing yourself elicits success by answering the following questions: 1. What has been the most important thing in making you successful at your job? 2. What advice would you give soon-to-be graduates? 3. How is marketing relevant to your role at Citynet? 4. What do you consider your personal brand to be? Woven into the chapter, you see how Michael later elaborates on: 1. The role of strategic planning in an organization (p. 31). 2. Why it’s important to clearly identify a firm’s target market (p. 38). |
learning objectives
LO 2-1 Discuss the importance of strategic planning for marketing.
LO 2-2 Outline the five main components of the marketing plan.
LO 2-3 Analyze the characteristics of an effective mission statement.
LO 2-4 Explain the elements of a situation analysis.
LO 2-5 Illustrate the major strategic directions a firm might take.
LO 2-6 Discuss the strategic decisions involved in reaching international consumers.
LO 2-7 Discuss the importance of strategic planning for nonprofit firms.
Key terms
competitive advantage (p. 41)
direct ownership (p. 46)
diversification (p. 40)
exporting (p. 44)
financial projections (p. 42)
franchising (p. 45)
joint venture (p. 46)
licensing (p. 45)
market (p. 34)
market development (p. 40)
market penetration (p. 39)
market summary (p. 34)
marketing plan (p. 31)
mission statement (p. 31)
multinational company (p. 38)
opportunities (p. 36)
positioning (p. 38)
product development (p. 39)
situation analysis (p. 34)
strategic planning (p. 31)
strategy (p. 37)
strengths (p. 35)
SWOT analysis (p. 35)
target market (p. 38)
threats (p. 36)
weaknesses (p. 35)
content outline
The following section provides the flow of information using the LEARNING OBJECTIVES as a guide, FIGURES and TABLES as visuals to elaborate on key areas, KEY TERMS learners will need to take away from the course and a notation of when to use POWERPOINT SLIDES with LECTURE NOTES to drive home teaching points. There is also a reminder on when CONNECT activities can be used, as well as tying in SOCIAL MEDIA IN ACTION to real-world applications of marketing products. This is created so that you can facilitate in-class or online discussion effectively.
| LO 2-1 | Discuss the importance of strategic planning for marketing. · The Importance of Strategic Planning | Key Terms: · Strategic planning | |||
| | PowerPoint Slides | Introductory Slides: LO 2-1: | Lecture Notes: · Whether you are marketing yourself or some other product, strategic planning can greatly increase the likelihood of success. · Strategic planning is the process of thoughtfully defining a firm’s objectives and developing a method for achieving those objectives. · Firms must continually undertake the task of strategic planning. · Shifting conditions, including changing customer needs and competitive threats, ensure that what worked in the past will not always work in the future, thus requiring firms to modify their strategy. · Strategic planning helps to ensure that marketers will select and execute the right marketing mix strategies to maximize success. | ||
| LO 2-2 | Outline the five main components of the marketing plan. · The Marketing Plan | Key Terms: · Marketing plan | |||
| | PowerPoint Slides | LO 2-2: | Lecture Notes: · A marketing plan is part of an organization’s overall strategic plan, which typically captures other strategic areas such as human resources, operations, equity structure, and a host of other non-marketing items. · The marketing plan is an action-oriented document or playbook that guides the analysis, implementation, and control of the firm’s marketing strategy. · Creating a marketing plan requires the input, guidance, and review of employees throughout the various departments of a firm, not just the marketing department. · The specific format of the marketing plan differs from organization to organization. · Most plans include an executive summary, situation analysis, marketing strategy, financials section, and controls section. | ||
| LO 2-3 | Analyze the characteristics of an effective mission statement. · Mission Statement · Executive Summary | Key Terms: · Mission statement | |||
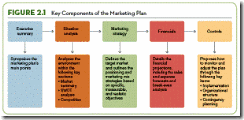
| | Figure 2.1 | Figure Information: Key Components of the Marketing Plan
The five components of the marketing plan are interlinked and connected. Each of the components should be grounded in the firm’s overall mission, which is ideally defined in a clear and succinct mission statement. | Insight Questions: 1. Who is involved in developing the marketing plan? (Answer: Most departments in a firm, not just the marketing department.) 2. What types of objectives should be considered in the marketing strategy? (Answer: specific, measurable and realistic objectives.) 3. Should a marketing plan have a short-term or long-term vision? (Answer: Both; and they should tie into the organization’s mission for long-term sustainability.) | ||
| | PowerPoint Slides | LO 2-3: | Lecture Notes: · The first step in creating a quality marketing plan is to develop an effective mission statement. · A mission statement is a concise affirmation of the firm’s long-term purpose. · An effective mission statement provides employees with a shared sense of ambition, direction, and opportunity. · A firm should begin the process of developing a mission statement by considering the following classic questions: o What is our business? o Who is our customer? o What is our value to the customer? o What will our business be? o What should our business be? · The firm should then focus on instilling the three primary characteristics of a good mission statement: o The mission statement should focus on a limited number of goals. o The mission statement should be customer oriented and focused on satisfying basic customer needs and wants. o Mission statements should capture a shared purpose and provide motivation for the employees of the firm. · A firm’s mission statement drives many of the other decisions it makes, including how best to market its goods and services to consumers. · A sound mission statement provides a basis for developing the marketing plan and provides a standard to ensure that the business never strays too far from its core goals and values. · The executive summary serves as the elevator pitch for the marketing plan. · It provides a one- to two-page synopsis of the marketing plan’s main points. · While the executive summary is listed first, firms should complete this part of the marketing plan last. | ||
| LO 2-4 | Explain the elements of a situation analysis. · Situation Analysis o Market Summary § BCG Matrix o SWOT Analysis § Internal Considerations § External Considerations o Competition | Key Terms: · Situation analysis · Market · Market summary · SWOT analysis · Strengths · Weaknesses · Opportunities · Threats | |||
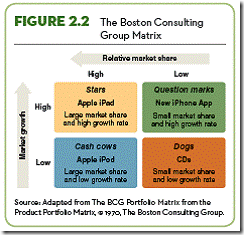
| | Figure 2.2 | Figure Information: The Boston Consulting Group Matrix
The BCG matrix (1970) combines the two elements of market growth and relative market share to produce four unique product categories—stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs—each requiring a different marketing strategy. | Insight Questions: 1. What does the BCG Matrix determine? (Answer: where the product will fall in the marketplace; this serves as a starting point for developing marketing strategies to address that market position.) 2. What quadrant would represent the Apple iPad? (Answer: cash cow.) 3. What quadrant would represent a new iPhone application? (Answer: question mark.) | ||
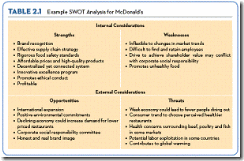
| | Table 2.1 | Table Information: Example SWOT Analysis for McDonald’s Companies like McDonald’s often complete a SWOT analysis to identify and evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Evaluating internal and external considerations is extremely important in determining a firm’s position and competitive advantage. | Insight Questions: 1. Which elements of a SWOT analysis are internal considerations? (Answer: strengths and weaknesses.) 2. Which elements of a SWOT analysis are external considerations? (Answer: opportunities and threats.) 3. What key words or action-oriented words do you see in the example? (Answer: effective, rigorous, flexible, promotes, positive, contributes.) 4. What qualitative and quantitative measures exist in the example SWOT analysis? (Answer: open-ended.) | ||
| | PowerPoint Slides | LO 2-4: | Lecture Notes: · A situation analysis is the systematic collection of data to identify the trends, conditions, and competitive forces that have the potential to influence the performance of the firm and the choice of appropriate strategies. · The situation analysis comprises three subsections: market summary, SWOT analysis, and competition. · The market summary sets the stage for the situation analysis section by focusing on the market to which the firm will sell its products. A market is the group of consumers or organizations that is interested in and able to buy a particular product. · The market summary describes the current state of the market. · The market summary would also consider the growth opportunities internationally and potential sales through international expansion. · One of the most popular analysis tools to describe the current market is The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix. · The BCG matrix combines the two elements of market growth and relative market share to produce four unique product categories—stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs—each requiring a different marketing strategy. · Star products combine large market share with a high growth rate. · Cash cows are products that have a large market share in an industry with low growth rates. · Question marks have small market share in a high-growth industry. · Dogs are products that have small market share in industries with low growth rates. · The evaluation of a firm’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is called a SWOT analysis. · The strengths and the weaknesses aspects of the analysis focus on internal characteristics. o Strengths are internal capabilities that help the company achieve its objectives. o Weaknesses are internal limitations that may prevent or disrupt the firm’s ability to meet its stated objectives. · The opportunities and threats aspects of the SWOT analysis focus on the external environment. · Opportunities are external factors that the firm may be able to capitalize on to meet or exceed its stated objectives. · Threats are current and potential external factors that may challenge the firm’s short- and long-term performance. · While most marketing plans examine direct competitors thoroughly, indirect competitors typically receive far less attention or are overlooked entirely. · Indirect competitors can take market share away from a firm as macro trends or consumer preferences change. | ||
| | Connect Assignment 2-1 | Topic: SWOT Analysis By identifying which elements of a fictional company’s situation analysis fall into each category, you will understand the key differences among each of the four SWOT components. Incorporate This Activity into Your Course. For tips on how to incorporate this Connect exercise into your lesson, click here to access the Interactive Assignment Guide. Insight Questions: 1. In a real SWOT analysis, what resources will you use to compose your SWOT analysis? 2. For measurement and analysis, figure out which elements are quantitative, and which ones are qualitative. 3. When should a SWOT analysis be conducted? Think in terms of frequency, product development and strategic planning. | |||
| LO 2-5 | Illustrate the major strategic directions a firm might take. · Marketing Strategy o Target Markets and Positioning o Strategic Decisions § Market Penetration § Product Development § Market Development § Diversification o Marketing Mix § Product § Promotion § Distribution § Pricing · Financials · Controls | Key Terms: · Strategy · Target market · Multinational company · Positioning · Market penetration · Product development · Market development · Diversification · Competitive advantage · Financial projections | |||
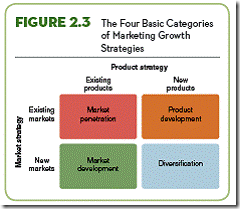
| | Figure 2.3 | Figure Information: The Four Basic Categories of Marketing Growth Strategies
A company’s marketing strategy can follow various paths based on the product and industry, but most seek to move the product in one of the four directions: market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification. Each of these categories represents the intersection of a strategy related to products and another related to markets. | Insight Questions: 1. Which strategy involves encouraging current customers to buy more each time they patronize a store or to buy from the store on a more frequent basis? (Answer: market penetration.) 2. Which strategy did Dr Pepper Ten use in their campaign launch “It’s not for women”? (Answer: product development.) 3. Which strategy focuses on selling existing goods and services to new customers? (Answer: market development.) 4. List three examples of companies that have used the diversification strategy. (Answer: Disney, open-ended.) | ||
| | PowerPoint Slides | LO 2-5: | Lecture Notes: · A strategy is the set of actions taken to accomplish organizational objectives. · A successful marketing strategy can lead to higher profits, stronger brands, larger market share, and a number of other desired outcomes for stakeholders of the organization. · The marketing strategy component of the marketing plan lists the actions the firm must take to accomplish the marketing objectives it established in its mission statement and strategic planning process. The effectiveness of the marketing strategy depends in part on the clarity of the short- and medium-term objectives the firm has defined. · Quality marketing objectives have three basic characteristics: o Specific o Measurable o Realistic · Developing specific, measurable, and realistic marketing objectives provides a good basis for companies as they seek to identify a target market and correctly position their product for that market. · A target market is the group of customers toward which an organization has decided to direct its marketing efforts. · Small firms may have only one target market; large organizations might enter multiple target markets. · A firm with multiple target markets that operates in two or more countries is called a multinational company. · Regardless of size, firms tend to enter multiple markets by first serving one group and then expanding based on success with that group. · Success within the target market depends, to some degree, on how the firm positions its product. · Positioning refers to the activities a firm undertakes to create a certain perception of its product in the eyes of the target market. · To position its product, a firm must take into consideration issues such as the competition, the needs and wants of the target market, and the element of mystique or drama that the good or service naturally has. · A company’s marketing strategy can follow various paths based on the product and industry, but most seek to move the product in one of four directions: o Market penetration strategies emphasize selling more of existing goods and services to existing customers. o Product development strategies involve creating new goods and services for existing markets. o Market development strategies focus on selling existing goods and services to new customers. o Diversification strategies seek to attract new customers by offering new products that are unrelated to the existing products produced by the organization. · The final aspect of the marketing strategy section of the marketing plan focuses on determining how each element of the marketing mix will support the chosen strategy. · The product section of the marketing plan comprises a detailed description of the product being offered, not only the good or service itself, but also any related services like warranties and guarantees that accompany the good or service. · A product possesses a competitive advantage when it enjoys a superior position over competing products because consumers believe it has more value than other products in its category. · The promotion section details how the organization will communicate the value of its product. · This section builds on the strengths of the product section and references the specific promotional tools—advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, or public relations—the organization will use to reach its target market. · Distribution strategies fall within the place marketing mix element. · The distribution section of the marketing plan describes how the firm will deliver value to its customers. · The pricing section of the marketing plans specifies how much money customers must pay for the product and describe why that price was selected. · The overall profitability of both the product and the firm can be found in the financial section of the marketing plan. · Financial projections provide those reading the plan with a bottom-line estimate of the organization’s profitability. · Financial projections can include numerous items, but all should contain a sales forecast (or fundraising projections for a nonprofit), an expense forecast, and a break-even analysis. · The final section in most marketing plans outlines the controls the firm will put in place to monitor and adjust the plan as the firm executes on the strategy laid out in it. · The controls section should include implementation, organizational structure, and contingency planning. | ||
| | Connect Assignment 2-2 | Topic: Strategic Directions By identifying which company used each particular strategy, you will understand how all of the strategies may impact your future employer.
Incorporate This Activity into Your Course. For tips on how to incorporate this Connect exercise into your lesson, click here to access the Interactive Assignment Guide. Insight Questions: 1. Which strategies can be used to enter into international markets? 2. List two examples of organizations that have implemented each one of the four strategies. Which strategy is easiest to identify? | |||
| LO 2-6 | Discuss the strategic decisions involved in reaching international consumers. · Marketing Strategy in a Global Context o Exporting o Licensing o Franchising o Joint Venture o Direct Ownership | Key Terms: · Exporting · Licensing · Franchising · Joint venture · Direct ownership | |||
| | Figure 2.4 | Figure Information: International Market Entry Strategies
As part of developing a marketing plan that involves global marketing, firms must choose from among the following five major strategic options for entering the international marketplace: exporting, licensing, franchising, joint venture, or direct investment. Each offers a unique mix of risk and reward. | Insight Questions: 1. What is the least risky option for entering international markets? (Answer: exporting.) 2. Which strategy offers marketers the advantages of expanding the reach of their products quickly in a low-cost way? (Answer: licensing.) 3. Which strategy is an attractive method of entering foreign markets because its licensees assume the majority of the capital costs and human resource issues? (Answer: franchising.) 4. Which strategy works best when the partners’ strategic goals align, their competitive goals diverge, and they are able to learn from one another without infringing on each other’s proprietary skills? (Answer: joint venture.) 5. What is the riskiest method of entering an international market? (Answer: direct ownership.) | ||
| | Connect Assignment 2-3 | Topic: Social Media By understanding the role social media can play in achieving your objectives, you will be able to apply these strategies to successfully implement a marketing plan for your organization in the years ahead. Incorporate This Activity into Your Course. For tips on how to incorporate this Connect: Social Media in Action exercise into your lesson, click here to access the Interactive Assignment Guide. Insight Questions: 1. Should social media strategies always be included in a company’s marketing plan since it is a popular medium? 2. How would you determine the social media platform a company should use (i.e. Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Vine, Pinterest, etc.)? Should a given company use all of them? | |||
| | Social Media in Action | Example: Procter and Gamble (P&G)
Procter and Gamble (P&G) was looking for a way to reverse flat or declining sales of its Pepto-Bismol product in 2010. Marketing research suggested that Pepto-Bismol was most commonly discussed on social media during Saturday and Sunday mornings. To attract consumers to the brand, P&G marketers increased the role of social media in their marketing plan with a Facebook campaign. Such success has prompted P&G to incorporate additional advertising on social media sites into its marketing plan for a variety of products. Such strategies have allowed P&G marketers to reach a new group of consumers and build deeper relationships with current customers. Insight Questions: 1. What types of posts does P&G make to their Facebook profile? 2. Do you follow organizations and their products/services on social media? If so, what type of information are you seeking? | |||
| | Connect Assignment 2-4 | Topic: International Marketing Approaches
By identifying an example of each strategy and its risk level, you will understand the potential risks and rewards of marketing your products globally. Incorporate This Activity into Your Course. For tips on how to incorporate this Connect exercise into your lesson, click here to access the Interactive Assignment Guide. Insight Questions: 1. What key factors determine the market strategy? 2. Do the same risks exist for small companies and large companies? 3. How do rewards differ for small and large companies? | |||
| | PowerPoint Slides | LO 2-6: | Lecture Notes: · The new reality of globalization means a firm’s strategic planning process must include a discussion about what, if any, international presence the firm wants to pursue. · One of the most critical strategic decisions involves how to enter foreign markets. · The firm must choose from among the five major strategic options for entering the international marketplace: exporting, licensing, franchising, joint venture, or direct investment. · Each offers a unique mix of risk and reward. · Typically, the least risky option for entering international markets is exporting. · Exporting is selling domestically produced products to foreign markets. · Increasingly, firms of all sizes export their products to other countries. · Licensing offers marketers the advantages of expanding the reach of their products quickly in a low-cost way. · Licensing is a legal process in which one firm pays to use or distribute another firm’s resources, including products, trademarks, patents, intellectual property, or other proprietary knowledge. · The use of licensing to enter international markets has increased significantly in recent years due to several factors, including more regulation, rising research and development (R&D) costs, and shortened product life cycles. · Franchising is a contractual arrangement in which the franchisor provides a franchisee (local owner operator) the right to use its name and marketing and operational support in exchange for a fee and, typically, a share of the profits. · A riskier option than exporting, licensing, or franchising is a joint venture. · In a joint venture, a domestic firm partners with a foreign company to create a new entity, thus allowing the domestic firm to enter the foreign company’s market. · Joint ventures, however, can result in mistrust over proprietary knowledge, conflict over new investments, and disagreements about how to share revenue and profits. · The riskiest method of entering an international market is direct ownership , which requires a domestic firm to actively manage a foreign company or overseas facilities. · Direct ownership is a good strategic option when the firm sees substantial sales potential in the international market, very little political risk, and similarities between the foreign and domestic cultures. · Marketers should diligently and thoroughly analyze the risks and rewards of each type of foreign entry as they develop their marketing plan. | ||
| LO 2-7 | Discuss the importance of strategic planning for nonprofit firms. · Strategic Planning for Nonprofit Organizations | Key Terms: (none) | |||
| | PowerPoint Slides | LO 2-7: Supplemental Slides: | Lecture Notes: · Though some aspects of a nonprofit marketing plan may differ from that of a for-profit firm, the main components and overall structure remain the same. · Nonprofit marketers should pay especially close attention to the implementation and accountability sections of the marketing plan, as most work on a very tight marketing budget, making every dollar spent a critical investment. | ||
today’s professional
| Erin Blankenship Development Coordinator, Harmony Health Clinic
Erin Blankenship, a recent college graduate, explains how flexibility, self-motivation and networking can further your career. Personable and creative, she provides insight by answering the following questions: 1. Describe your job. 2. Describe how you got the job you have. 3. What has been the most important thing in making you successful at your job? 4. What advice would you give soon-to-be graduates? 5. What do you consider your personal brand to be? |
marketing plan exercise
Your Marketing Plan. The next step in developing a full marketing plan for yourself is to conduct a SWOT analysis on yourself that ties back to the objectives you developed at the end of Chapter 1. Be sure to think through each element honestly and assess where you are today. This will help focus you on what you need to accomplish over the rest of your college career. Strategically assess the following areas:
· Strengths
· Weaknesses
· Opportunities
· Threats
discussion questions
1. Find mission statements from five Fortune 500 companies, then rank them from best (1) to worst (5) and discuss why you ranked them in that order. Which mission statements did you really like? How would you modify the mission statement you ranked last to make it better?
2. Conduct a SWOT analysis for your college or university. List three to five strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for your school.
3. Select a marketing strategy implemented by a large firm or nonprofit organization that you think was effective. Describe why you liked the strategy. Identify which of the strategic directions discussed in this chapter best reflects the strategy you chose.
4. Select two businesses you frequent (e.g., restaurants, clothing stores, grocery stores, etc.). Who is their target market? Then identify at least two competitors (either direct or indirect) for each business. Describe how the two businesses you selected position themselves in the market relative to their competitors. Which one of the two businesses does a better job positioning its products to its target market? Explain your answer.
5. Is marketing your products globally always a good decision? Discuss your answer and provide examples of firms that have both succeeded and failed in international markets.
social media application
Analyze the social media presence of your college or university using the following questions and activities as a guide:
1. In your opinion, is your institution doing a good job marketing the school through social media?
2. What grade would you give your school’s efforts and why?
3. Provide at least two specific recommendations for how your school could improve its social media marketing presence. In addition, provide an example of a university that is doing a better job of marketing through social media than your school and describe what it does.
ethical challenge
Bank of America announced in 2011 that it was considering introducing a $5 fee for some debit card users. They also introduced several types of accounts that required users to pay fees unless they kept minimum balances in the accounts, made regular deposits, or used credit cards. Driving revenue that benefits shareholders and employees at the possible expense of banking’s most vulnerable customers presents marketers with an ethical dilemma. Use the ethical decision-making framework to answer the following questions:
1. What are the major ethical issues involved in Bank of America’s decision? Who are the affected stakeholders? How will those stakeholders be affected?
2. If you were a competitor of Bank of America, what would your marketing strategy be for dealing with the new Bank of America fee?
3. How is Bank of America positioned in the marketplace? Does this fee reinforce the image it is seeking to create?
video case
Please go to Connect to access the video case featuring Ford Motor Company that accompanies this chapter.
Incorporate This Video into Your Course. For tips on how to incorporate this video case into your lesson, click here to access the Interactive Assignment Guide.
career tips
To help you think about how to market yourself and develop your social skills, follow these insights.
| Michael Friloux, Senior Vice President of Business Development at Citynet, encourages you to spend time considering two things that many college graduates don’t fully appreciate: the power of questions and the importance of people skills.
1. The Power of Questions: When in doubt, always ask the question. 2. The Importance of People Skills: It’s important to cultivate positive and productive interactions with everyone you work with. |
Connect Instructor’s Manual
Helpful Suggestions Regarding Assignment Policies: Connect gives instructors a wide array of flexibility in making assignments and creating grading policies. Instructors may choose to:
· Assign as many assignments as he/she deems appropriate.
· Determine point values for each question/interactive individually.
· Make available multiple attempts per assignment with options of accepting the highest score or averaging all the attempts together.
· Deduct points for late submissions of assignments (percentage deduction per hour/day/week/etc.) or create hard deadlines.
· Show feedback on interactives/questions immediately or at the time of his/her preference.
· Create new assignments or questions from scratch, such as web-linked assignments, LearnSmart study modules, writing assignments, blog assignments, discussion board assignments, or upload questions from a pool.
Recommendations: Here are some recommendations you might want to consider if you are using Connect for the first time.
· Assigning Learning Objective Videos: Learning Objective Videos are designed to reinforce core concepts in the chapter. These are assignable by Learning Objective and require students to view a brief video customized to match the content in the book. After watching the video, students are tested on their understanding of these concepts through 4–6 Concept Check questions. It is recommended that you assign Learning Objective Videos before class to help generate class discussion. You can choose to have this feature feed the gradebook.
· Assigning Interactives: Consider assigning only 1 or 2 interactives per chapter.
· Pooling Interactives: You have the option of “pooling” questions from three groups of questions (a, b, and c). Choosing all three questions and assigning them as “pools” allows Connect to serve up a different version of the interactive to different students. In this way, two students working the “same problem” might have slightly different versions. This provides a higher level of integrity of students’ individual work. Setting up question pools is recommended.
· 
· The entire LearnSmart module is available to your student at all times; however, assigning 30 minutes or so will prompt students to try it. You are required to select a due date for LearnSmart. However, this will not bar the student from LearnSmart access; it is designed to show you that the student has taken the LearnSmart assignment. LearnSmart is an adaptive study tool designed for students. It can also show you where students are struggling to understand specific concepts.
· The student’s LearnSmart score in the Connect reports is based on her or his mastery of the material at the time the assignment is due. Mastery is an evaluation of the number of learning objectives a student completed via performance on answering questions.
· Students may, and are encouraged to, continue to use LearnSmart throughout the semester. After the assignment due date, they can continue to access LearnSmart. Continued use of LearnSmart will not affect their LearnSmart assignment results in the Connect reports, but has been shown to improve test scores by as much as a full letter grade.
Time-Saving Hints:
· Instructors may want to give students unlimited or multiple attempts on the first few assignments so the students have a chance to learn and navigate the system before selecting the option for one attempt only.
· 
· Each interactive has several different versions of the same material/questions to prevent students from copying answers directly from one another. It might be wise to assign different versions to different sections or select “scramble” assignment questions.
· Feedback given to students is time flexible. Selecting feedback to be displayed after the assignment due date helps to prevent students from giving the correct answers to other students while the interactive is still available.
Connect: Chapter 2 Interactive Assignment Guide
Interactives:
Interactive Assignment 2-1
Interactive Assignment 2-2
Interactive Assignment 2-3: Social Media in Action
Interactive Assignment 2-4
Video Case featuring Ford Motor Company
Chapter Learning Objectives:
LO 2-1 Discuss the importance of strategic planning for marketing.
LO 2-2 Outline the five main components of the marketing plan.
LO 2-3 Analyze the characteristics of an effective mission statement.
LO 2-4 Explain the elements of a situation analysis.
LO 2-5 Illustrate the major strategic directions a firm might take.
LO 2-6 Discuss the strategic decisions involved in reaching international consumers.
LO 2-7 Discuss the importance of strategic planning for nonprofit firms.
Interactive Assignment 2-1
Applying a SWOT Analysis
Activity Summary: This activity involves developing a SWOT analysis for an organization. Students will be presented with various descriptions, and they must determine whether each is a strength, weakness, opportunity, or threat. A concept review includes a discussion of the differences between the internal and external elements of a SWOT analysis.
Learning Objectives:
LO 2-4 Explain the elements of a situation analysis.
Difficulty: 2 Medium
AACSB: Analytic
Blooms: Understand
Page reference in text: 37
Follow-Up Activity: Instructors could discuss the SWOT analysis of a local business that the students are familiar with. Students could be asked to consider an organization where they have worked or volunteered and develop a SWOT analysis for it. Instructors could also engage students in a debate or assignment over what are the biggest opportunities and threats for the students’ careers in the months and years ahead.
Interactive Assignment 2-2
Identifying Strategic Directions
Activity Summary: This activity involves different strategic directions that an organization can choose. Students will be presented with a list of recent marketing decisions, and then be asked to categorize each decision into the specific strategic direction that was chosen. A concept review follows with a discussion of the four basic categories of marketing strategies.
Learning Objectives:
LO 2-5 Illustrate the major strategic directions a firm might take.
Difficulty: 2 Medium
AACSB: Analytic
Blooms: Understand
Page reference in text: 41
Follow-Up Activity: Instructors could discuss recent decisions by popular companies such as Apple or Netflix, and what type of marketing strategy they used. Students could be asked to create a larger list of different companies that have implemented each of the different marketing strategies. Instructors could also engage students in a debate or assignment about which strategy would work best for a local company they are familiar with.
Interactive Assignment 2-3: Social Media in Action
Social Media as Part of a Marketing Plan
Activity Summary: This activity involves integrating social media into an overall marketing plan. Students will be presented with a fictional campus organization that they are President of, and asked to integrate social media into the various elements of the organization’s marketing plan. A concept review includes a discussion of the different components of a marketing plan.
Learning Objectives:
LO 2-2 Outline the five main components of the marketing plan.
LO 2-4 Explain the elements of a situation analysis.
LO 2-5 Illustrate the major strategic directions a firm might take.
Difficulty: 2 Medium
AACSB: Analytic
Blooms: Understand
Page reference in text: 43
Follow-Up Activity: Instructors could discuss the increasing use of social media marketing by organizations of all types and sizes. Students could be asked what components of the marketing plan they think are best suited for social media tools. Instructors could also engage students in a debate or assignment where they have to find examples of how organizations have used different social media platforms (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, etc.) for different parts of a marketing plan.
Interactive Assignment 2-4
Entering International Markets
Activity Summary: This activity involves the major global entry strategies for marketers looking to sell their products internationally. Students will be presented with a list of the market entry strategies and asked to put them in order relative to the risk level that is associated with each. A concept review includes a discussion of the five major global entry strategies used by marketers.
Learning Objectives:
LO 2-6 Discuss the strategic decisions involved in reaching international consumers.
Difficulty: 2 Medium
AACSB: Analytic
Blooms: Understand
Page reference in text: 46
Follow-Up Activity: Instructors could discuss examples of popular businesses that have used each type of global market entry strategy. Students could be asked to create a larger list of individual companies that have used each of the different strategies and discuss the success or failure of each. Instructors could also engage students in a debate or assignment involving which market entry strategy the students think is best for today’s economic environment and why.
Video Case featuring Ford Motor Company
Planning for Success: Ford Fusion
Activity Summary: This activity involves the successful marketing strategy for the Ford Fusion. Students will be presented with a video case discussing Ford’s marketing plan for the Fusion and several strategic decisions the company made. A concept review follows with multiple choice questions throughout the video.
Learning Objectives:
LO 2-1 Discuss the importance of strategic planning for marketing.
LO 2-2 Outline the five main components of the marketing plan.
LO 2-4 Explain the elements of a situation analysis.
Difficulty: 3 Hard
AACSB: Analytic
Blooms: Apply
Page reference in text: 52
Follow-Up Activity: Instructors could discuss the success of the Ford Fusion’s marketing plan and Ford’s successful turnaround as a company in recent years. Students could be asked to create a larger list of strategic decisions for other types of automobile products. Instructors could also engage students in a debate or assignment involving which automobile companies, in their opinion, have made the best marketing decisions in recent years.



















No comments:
Post a Comment